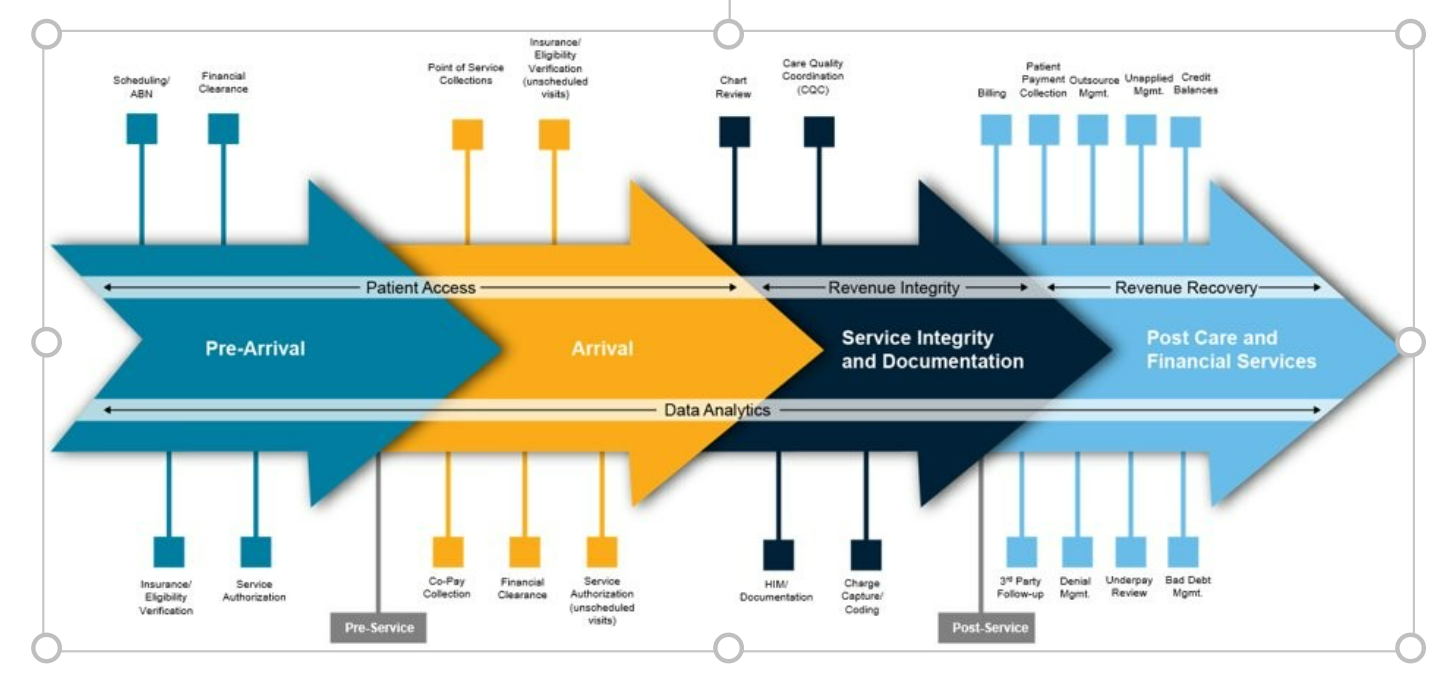
With decades of experience, Baker Tilly has the breadth and depth of knowledge needed to help evaluate and transform any portion of your organization’s revenue cycle operations. Whether it’s assessing current processes, addressing specific inefficiencies of your RCM operations, or conducting a full-scale revenue cycle transformation, our team of specialists are here to help during any of the following revenue cycle stages.
Breaking down the revenue cycle process
Pre-arrival
(scheduled visits)
Arrival
(scheduled and unscheduled visits)
Service Integrity and Documentation
(scheduled visits)
There are several steps and activities that take place before the patient arrives at the hospital in order to secure payment from the insurance company and/or the patient.
Contract negotiation: Determining reimbursement and compensation rates with health plans.
Scheduling/Advanced beneficiary notice (ABN): Entering the patient into the EMR system and sending out an ABN if the customer is a Medicare recipient.
Insurance/Eligibility: Verifying the patient has insurance and is qualified to have the proposed procedure.
Financial clearance: Deciding if the patient can pay for the services, whether through insurance, out-of-pocket or financial assistance/charity.
Service authorization: Completing the necessary paperwork to submit the proposed procedure through the insurance company.
When arriving at the facility, there are additional steps taken before the procedure is provided. If this is an unscheduled visit (e.g., emergency department), some of the steps in the pre-arrival stage are also included during this phase.
Co-pay collection/point-of-service collections: Collecting co-pay or deductible, depending on if the patient is insured, or collecting cash up-front if uninsured. If the patient is a Medicare recipient, collecting payment for services or drugs not covered by Medicare or secondary insurance.
Financial clearance: Filling out the paperwork to pay for services or setting up a predetermined payment plan.
Insurance/Eligibility: If it is an unscheduled visit, verifying the patient has insurance and is qualified to have the proposed procedure. If this is a scheduled visit, conduct one last verification of eligibility.
Service authorization: If it is an unscheduled visit, completing the necessary paperwork to submit proposed procedure through insurance company.
Processes in the service integrity and documentation stage occur behind the scenes and are rarely seen by the patient (i.e., EMR systems, hospital host systems, patient journey activities, etc.).
Health information management (HIM)/Documentation: Receiving a medical record to begin coding.
Clinical documentation: Documenting the patient and procedure in the EMR system, includes discharge or after visit summary (seen by and discussed with patient).
Charge capture/Coding: Providing a diagnosis code, or multiple diagnosis codes, to justify the reason for the patient’s visit.
Charge description master (CDM) review: Auditing what is being coded and documented within the medical records for ensuring accuracy.
Clinical documentation improvement (CDI): Redeveloping workflows if documentation is inaccurate.
Post Care and Financial Services
The last phase of the revenue cycle process involves collecting the final payment and closing out outstanding accounts.
Contract review: Analyzing contracts for any discrepancies with payer contracts and documentation.
Billing: Sending out and automating notices of final payment from your facility.
Third-party follow-up: Collecting additional payments from insurance companies and other third parties.
Patient payment collection: Utilization of third-party vendors if there is an issue with collection of final payment from patient.
Outsource management: Outsourcing the collections process to help reduce accounts receivable (A/R).
Denial management: Flagging claims prior to submission to insurance company to prevent denials.
Cash application management: Providing select levels of interim management work to streamline collections process.
Payment variances: Identifying A/R balances that were underpaid or not paid appropriately.
Credit balances: Identifying A/R balances that were overpaid.
Bad debt management: Preventing and dealing with unpaid/outstanding account balances.
(scheduled and unscheduled visits)
Service integrity
and documentation
Post care and
financial services


Arrival
Pre-arrival

Pre-Service
Patient
Access


Revenue
Integrity
Revenue
Recovery





Post-Service










