

Motor
Battery
Motor
RISE OF EVs
While ICE cars still form a large share of sales in China, a record was set in the first quarter of 2025: nearly half of all new cars sold were NEVs.
�For two decades, China has been steering towards NEVs.
�From the mid-1980s, the government aimed to grow the traditional automotive industry as a key industrial pillar. Then, in the early 2000s, the focus shifted to NEVs.��This was not just about making vehicles, but building an ecosystem: supply chains, charging stations and more.��Thanks to these efforts – as well as subsidies – China’s largest carmakers have achieved major economies of scale, bringing down per-unit costs and edging out ICE vehicles.��Yet experts do not expect China’s new car market to grow much. S&P Global predicts 0 per cent to 3 per cent expansion in 2025 and 2026 as consumer demand remains weak, despite strong economic stimulus from the government. ��So carmakers have a new goal: conquering export markets.
�According to consultancy AlixPartners, China OEMs will take 30 per cent of global car sales by 2030, up from 21 per cent in 2024, with the major gains expected in emerging economies.
�
Meet the makers: China’s top car manufacturers
Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) control production facilities and brands. These huge companies have tens of thousands of employees and are often listed.
China’s automotive OEMs began to take off after the Second World War, when makers of military vehicles pivoted toward peacetime production.
From the 1980s, growth accelerated when the industry was deemed a major sector for development. This drove the rise of state-owned carmakers – including the Big Four of Changan, SAIC, FAW and Dongfeng – but also joint venture (JV) OEMs.
From 1979, foreign players had to have JVs with a local manufacturer as controlling partner. One of the first JVs was between American Motors Corporation and Beijing Automotive Industry Corporation, to build Jeeps.
A foreign automaker may have JVs with multiple local partners, such as FAW-Toyota or GAC-Toyota.
In 2022, the rules were relaxed to allow foreign entities majority ownership, to further boost investment appeal.
Top 10 OEMs
1
BYD
Geely
2
FAW-Volkswagen
3
Chery
4
SAIC-Volkswagen
5
Changan
6
SAIC-GM-Wuling
7
FAW-Toyota
8
GAC-Toyota
9
Great Wall
10
BYD Auto �Type: Subsidiary of publicly listed BYD�Founded: 2003
Headquarters: Shenzhen
Brands: BYD, Denza, Fangchengbao, Yangwang
Listing: BYD Company (Hong Kong, Shenzhen)
�
BYD was founded as a battery manufacturer by chemist Wang Chuanfu in 1995 and became the world’s second-largest. It started making cars in 2003 and is now the world’s top EV producer.
�It stands out for its vertical integration, with subsidiaries supplying many auto parts – as the group is also involved in electronic, semiconductors and related industries.
�BYD stopped selling ICE cars in 2022. Its NEVs have propelled it to the top of sales charts not just in China but also Singapore.
�

Zhejiang Geely Holding (Geely) �Type: Privately-owned company
Founded: 2003
Headquarters: Hangzhou, Zhejiang Brands: Farizon, Galaxy, Geely, LEVC, Lotus, Polestar, Proton, Radar, Smart, Volvo, Zeekr
Listings: Geely Auto (Hong Kong), Polestar (NYSE), Volvo (Nasdaq Stockholm)
�
Founded in 1986 as an appliance maker, Geely shifted to motorcycles and then cars in 1997. In the late 2000s, it began acquiring international car brands such as LEVC (formerly the London Cab Company), Swedish carmakers Volvo and Polestar, Malaysia’s Proton and Britain’s Lotus.
It also has its own brands: Galaxy, Farizon, Radar and Zeekr. Geely adopted platforms and tech from foreign brands to use across the group, giving it an advantage over rivals.�
�

FAW-Volkswagen �Type: Joint venture �Founded: 1991 �Headquarters: Changchun, Jilin �Brands: Audi, Jetta, Volkswagen �Owners: China FAW Group (60%), Volkswagen AG (25%), Volkswagen (China) Investment (10%), Audi AG (5%)
�
In a classic example of a domestic-foreign JV, pioneer carmaker First Automotive Works (FAW) paired European giant Volkswagen for this powerhouse.
The JV makes and sells vehicles from Audi and Volkswagen, as well as Jetta, a China-only marque that takes its name from VW’s mainstream sedan. It intends to launch 11 new China-specific models in 2026.��
�
Chery Automobile �Type: State-owned �Founded: 1997�Headquarters: Wuhu, Anhui �Brands: Chery, Exeed, Jaecoo, Jetour, Luxeed, Omoda,�Group owner: Wuhu municipal government
�
Set up by the Wuhu city government and funded by the Anhui provincial government, Chery’s first car was based on the Toledo sedan by Spanish carmaker Seat.
One of the first China OEMs to concentrate on foreign markets, and built its first overseas factory in Brazil in 2011. Its brands include Chery for mainstream cars, Exeed for premium SUVs and Jetour for mainstream SUVs.
Two of its brands, Omoda and Jaecoo, are aimed entirely at non-domestic markets and present in Singapore.�
�

SAIC-Volkswagen �Type: Joint venture �Founded: 1984�Headquarters: Anting �Brands: Audi, Skoda, Volkswagen �Owner: SAIC (50%), Volkswagen AG (39%), Volkswagen (China) Investment (10%), Audi AG (1%)
�
Established in 1984 and building cars since 1985, SAIC-Volkswagen is China’s oldest domestic-foreign JV automaker.
Formerly known as the Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation, SAIC is owned by the Shanghai municipal government. SAIC-VW differs from FAW-VW in that it also sells cars from mainstream Czech brand Skoda, which is part of the Volkswagen group.

Changan Automobile �Type: State-owned �Founded: 1862�Headquarters: Jiangbei, Chongqing�Brands: Avatr, Changan, Deepal, Kaicene �Group owner: State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council �Listing: Chongqing Changan Automobile Company (Shenzhen)
�
Changan’s origins lie in weapons maker Shanghai Foreign Gun Bureau, which produced Changjian 46, a jeep.
In the 1980s, the company produced its first passenger cars: licensed models from Suzuki. By the 2000s, Changan entered JVs with Suzuki, Ford, Mazda; within a decade, it successfully established its own Changan passenger car brand.
�

SAIC-GM-Wuling �Type: Joint venture �Founded: 2002�Headquarters: Liuzhou, Guangxi�Brands: Baojun, Wuling �Owner: SAIC (50.1%), General Motors (44%), Guangxi Auto (5.9%)
�This is China’s first automotive triple joint venture, between state-owned SAIC, US automaker General Motors and Guangxi Auto. The latter, formerly known as Wuling, produces minivans and small commercial vehicles.
�This JV made its mark with small, inexpensive minivans, and launched its own mainstream car brand Baojun in 2010.
�

FAW-Toyota �Type: Joint venture �Founded: 2002�Headquarters: Tianjin �Brands: Toyota �Owner: FAW (50%), Toyota (50%)
�Toyota, in its typical cautious style, entered its first China JV only in 2000, with Tianjin Automobile. Tianjin’s later acquisition by FAW turned the JV into FAW-Toyota.
The company initially concentrated on smaller, more mainstream Toyota models. But losing ground to domestic NEVs has prompted FAW and its JV partners to do more there too.�
�

GAC-Toyota �Type: Joint venture �Founded: 2004�Headquarters: Liuzhou, Guangxi�Brands: Audi, Skoda, Volkswagen �Owner: Guangzhou Automobile Group and Toyota Motor Corporation
�Guangzhou Automobile Group’s partnership with French carmaker Peugeot began in 1985 but imploded by 1995 on poor sales. After a successful partnership with Honda in 1998, GAC then began a JV with Toyota in 2004, propelling it further yet.�
�

Great Wall Motor �Type: Publicly listed company�Founded: 2002�Headquarters: Baoding, Hebei �Brands: GWM, Haval, Ora, Wey, Tank, Suou �Owner: Baoding Great Wall Holdings�Listed: Great Wall Motor (Hong Kong, Shanghai)
�Started as a vehicle repair workshop in 1976, Great Wall Motor made its own commercial vehicles in the 1980s and developed passenger cars by the 1990s.
It is now China’s largest maker of SUVs and pickup trucks. GWM is the main brand, with sub-brands Ora for EVs, Haval for mainstream SUVs, Wey for premium cars, Tank for luxury SUVs and Suou for motorcycles. GWM’s current chairman, Wei Jianjun, owns the majority of the company.��
�
China brands continue their rise
Before the 2020s, foreign brands dominated China’s domestic market. Now, the likes of Audi, BMW and Honda have lost their spots to local names.
With China supporting NEVs since the early 2000s – through subsidies, tax write-offs and more – numerous domestic EV brands have emerged.
Two decades later, China is now the world’s top NEV producer and also accounts for nearly two-thirds of global EV sales.
China brands’ cost-effective NEV models now dominate sales charts.
But the cut-throat competition has also driven a fierce price war, bankrupting smaller outfits and meaning depreciating used car values.
With EVs and local brands intertwined, both are predicted to continue growing their market share: S&P Global predicts EVs to rise from about 40 per cent of new car sales in 2024 to around 50 per cent in 2025-2026 and for local brands to take 60 per cent of the market in 2025, up from around 50 per cent in 2024. �
Best-selling models: Mass market hatches, premium EVs and petrol sedans
China’s EV shift is clear in how its top three best-selling models are cheap, compact EVs aimed at city-dwellers.
But the top 10 list also includes premium EVs such as the Tesla Model Y and Xiaomi SU7. Also notable is the continued popularity of sedans, even as the rest of the world turns towards SUVs.
Large sedans – including cars like the Volkswagen Sagitar and Nissan Sylphy – still sell well, as they remain a status symbol.
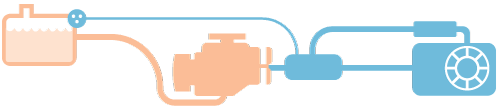
Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars are powered by gasoline or diesel engines.
But China is big on new energy vehicles (NEVs), which include:



Click on the boxes for more info
EV
PHEV
EREV
FUEL CELL
Electric vehicles (EVs) powered only by electricity
Plug-in hybrid EVs (PHEVs) and extended range EVs (EREVs) with both petrol engines and a battery. PHEVs can run on petrol; EREV engines only charge the battery and do not power the car directly.
Fuel cell vehicles that break down hydrogen to generate electricity, emitting only water.
Notes: Petrol-electric hybrids (non-plug-ins) are reported as ICE cars.�



Engine
Battery
Motor
Battery
Engine

Motor
Hydrogen tank
Fuel cell
China total passenger car sales by manufacturer 2023 to April 2025
Top selling China passenger car sales by brand 2023 to Apr 2025
Galaxy
1
Wuling
2
BYD
3
Xiaomi
4
Tesla
5
Volkswagen
6
Volkswagen
7
Geely
8
Volkswagen
9
Nissan
10
Galaxy�Model: Geome Xingyuan E22H�Fuel: EV Type: Mass market hatchback
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
Top 10 passenger car sales

Click on the boxes on the left for more info
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
117,115

Wuling�Model: Hongguang Mini�Fuel: EV Type: Mass market minivan
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
113,520

BYD�Model: Seagull �Fuel: EV Type: Mass market hatchback
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
110,943
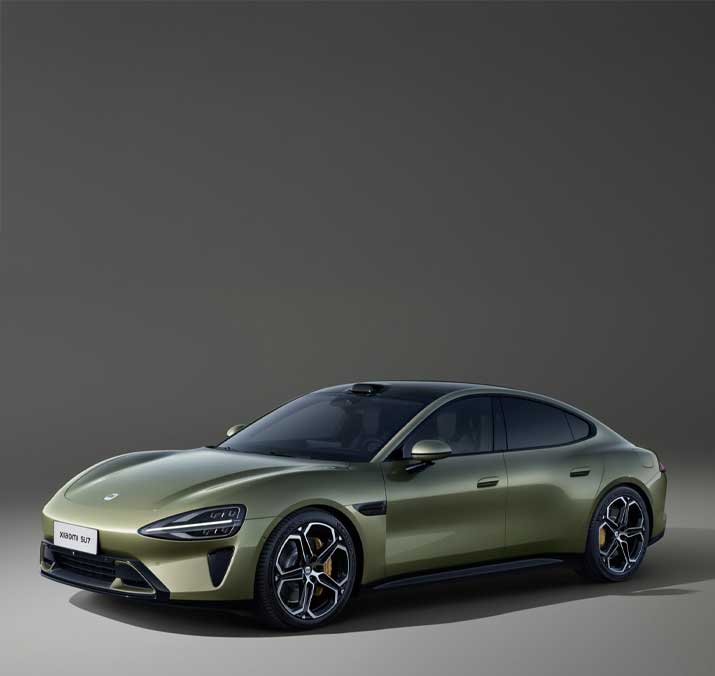

Xiaomi�Model: SU7�Fuel: EV Type: Premium sedan
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
104,372
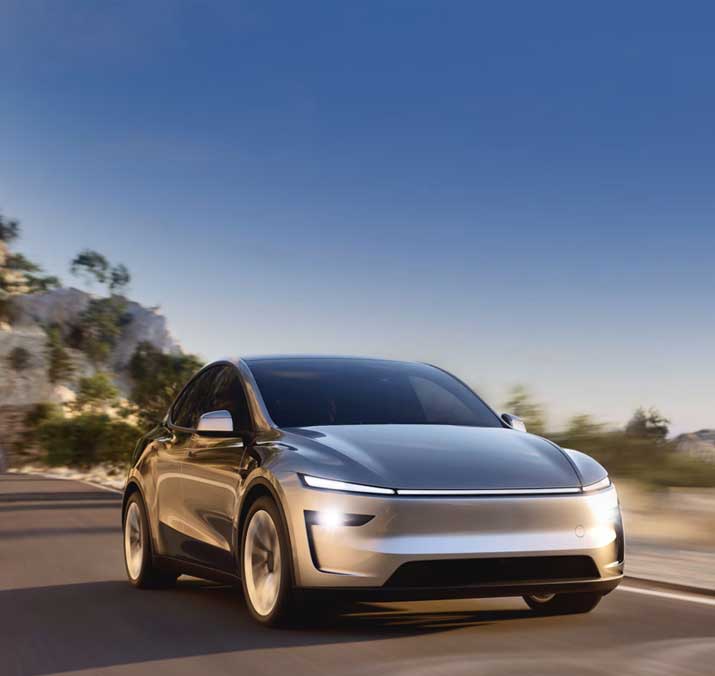

Tesla�Model: Model Y�Fuel: EV Type: Premium SUV
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
102,560
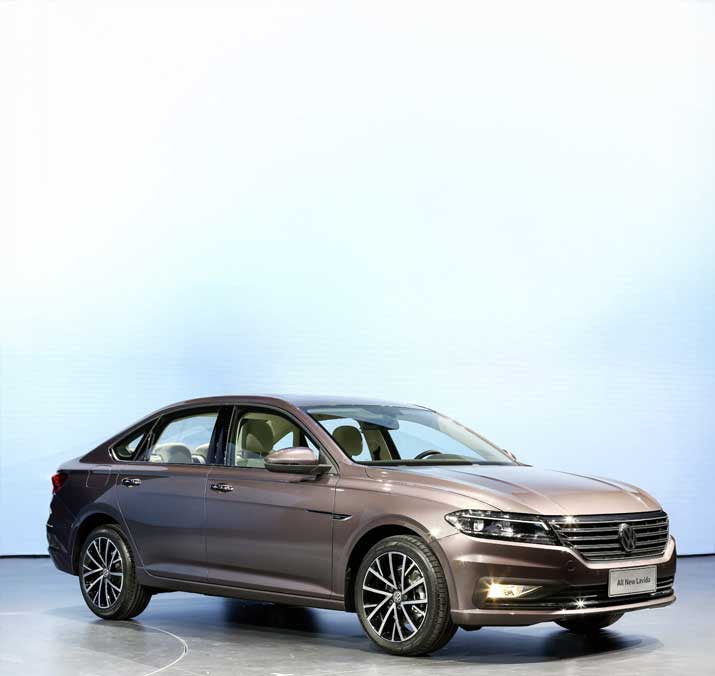

Volkswagen�Model: Lavida�Fuel: ICE Type: Mass market sedan
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
89,099

Volkswagen�Model: Passat
Fuel: ICE Type: Mass market sedan
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
79,258
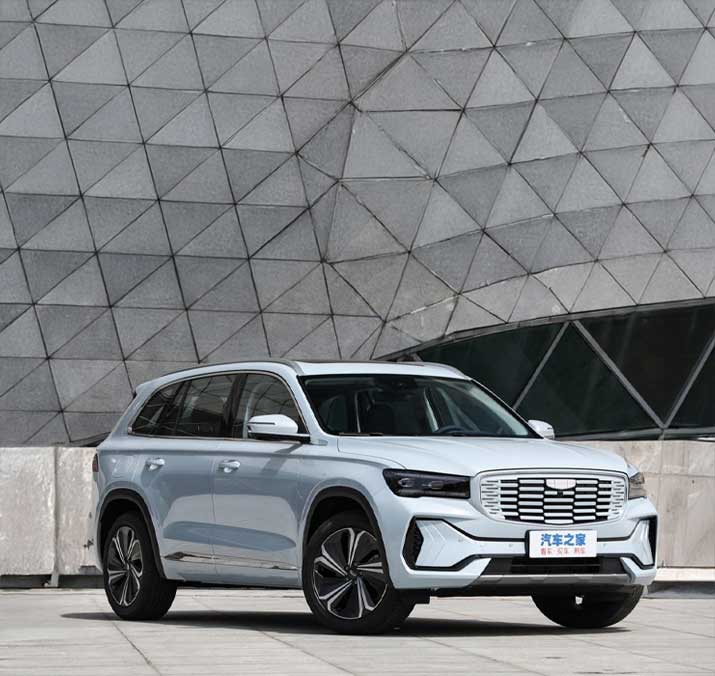

Geely�Model: Xingyue L�Fuel: ICE Type: Mass market SUV
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
74,179
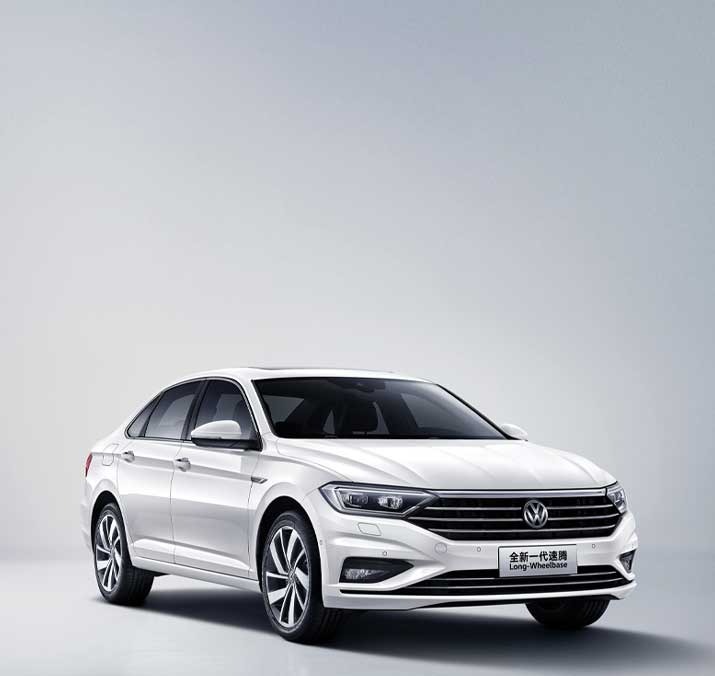

Volkswagen�Model: Sagitar�Fuel: ICE Type: Mass market sedan
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
73,973
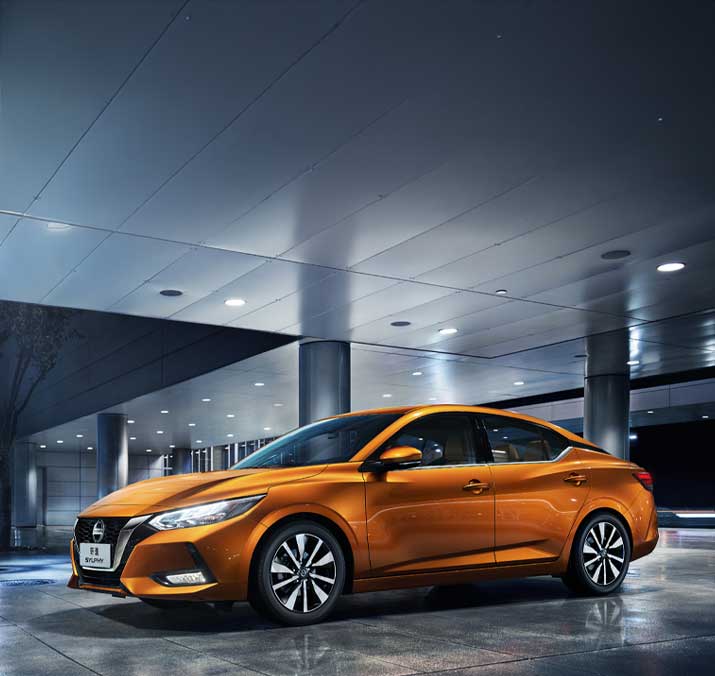

Nissan�Model: Sylphy�Fuel: ICE Type: Mass market sedan
Jan to Apr 2025 sales:
The top three best-selling models are all inexpensive, compact BEV hatchbacks, coming in at under 70,000 yuan (S$12,562). As S&P Global notes, affordability is the key to mass-market success in China.
70,334
Charger
Fuel tank
Charger
Fuel tank
Battery
What’s on the road?
China domestic market passenger car sales, 2023 to Apr 2025
2023
2024
Jan - Apr 2025
SOURCE: CHINA AUTOMOTIVE RESEARCH FIRM THINKERCAR PHOTOS: MANUFACTURERS, ADOBE STOCK GRAPHIC: HYRIE RAHMAT, MARIO MONREAL, BT
Charger


Motor
Fuel tank
Battery
Engine



Motor
Engine
Battery
Fuel tank
Charger


Motor
Battery
Hydrogen tank
Fuel cell
Fuel tank




Best-selling models: Mass market hatches, premium EVs and petrol sedans
Xiaomi Su7
Galaxy Geome Xingyuan
BYD Seagull
Plug-in hybrid EVs (PHEVs) and extended range EVs (EREVs) with both petrol engines and a battery. PHEVs can run on petrol; EREV engines only charge the battery and do not power the car directly.
Plug-in hybrid EVs (PHEVs) and extended range EVs (EREVs) with both petrol engines and a battery. PHEVs can run on petrol; EREV engines only charge the battery and do not power the car directly.
2023
2024
Jan - Apr 2025
Hover over the bars for details
Circle sizes reflect relative share within each year, not absolute numbers
Note: NEV is made up of EV, EREV, FUEL CELL and PHEV