The publication of this promotional infographic was supported and funded by argenx.

Polyneuropathy (CIDP): Reveal The Unseen Burden
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating

Neurology


This content is exclusively intended for healthcare professionals practicing in the UK, EU, Iceland, Norway, Canada, Australia & Liechtenstein only

Introduction
CIDP is a rare, often progressive, immune-mediated neuromuscular disorder of the peripheral nervous system.1
As an acquired inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy, it can lead to both distal and proximal weakness, along with sensory deficits.1 The condition typically causes motor and sensory impairment in the upper and lower limbs.2




The incidence of CIDP is approximately twice as common in males than females.1
Onset may occur at any age but is more common between 40-60 years,1 with incidence and prevalence increasing with age.3

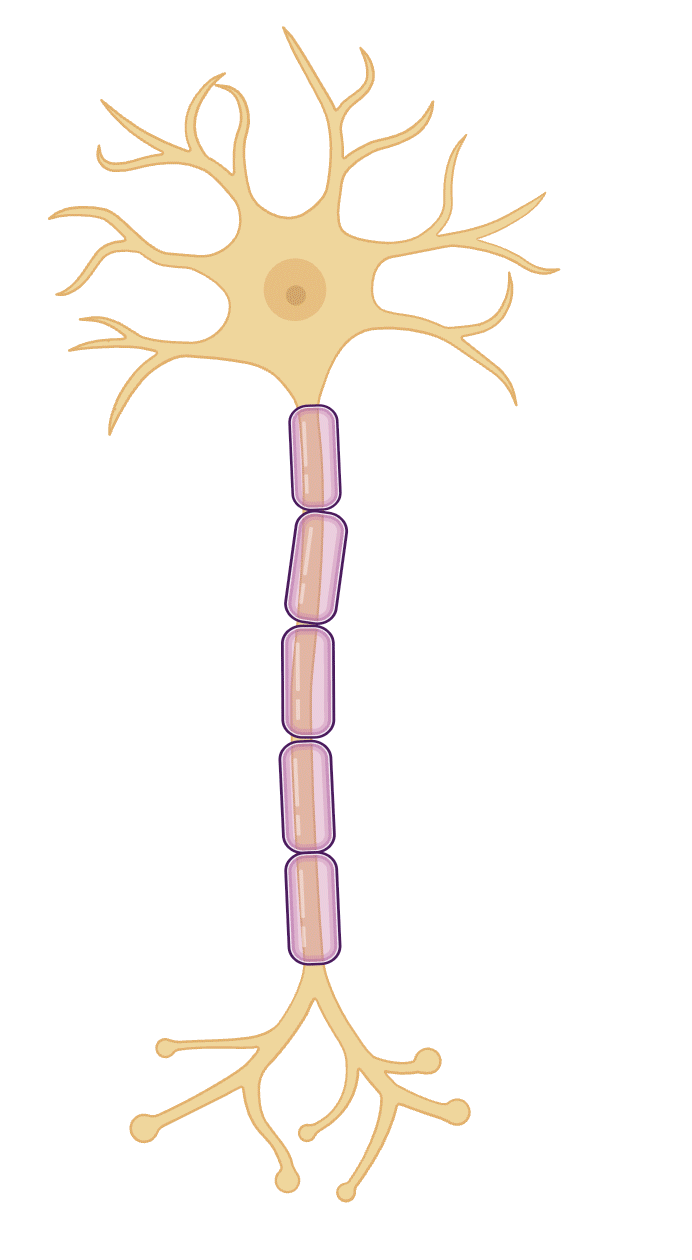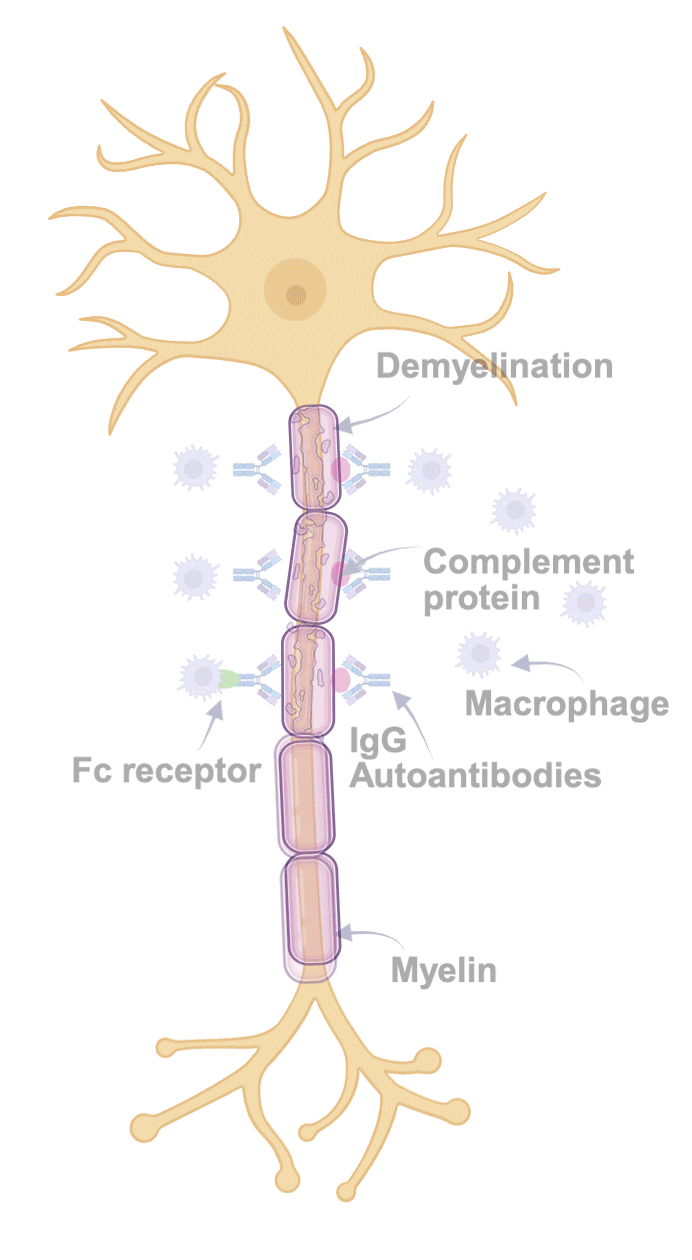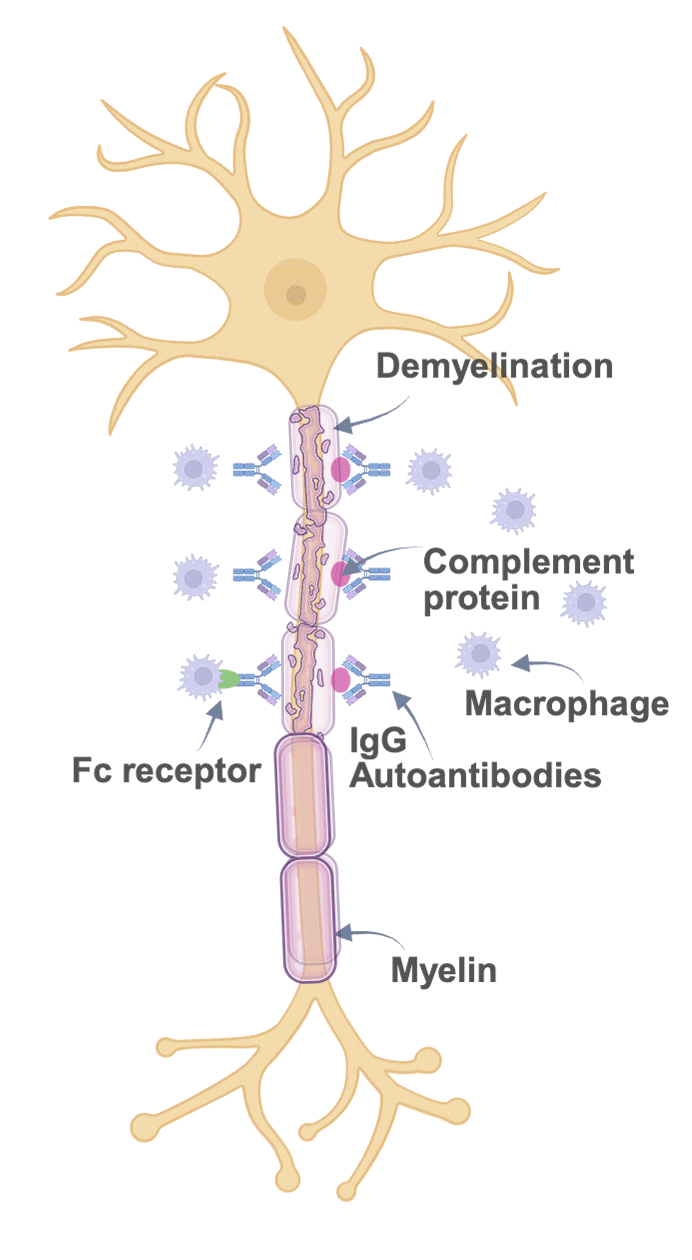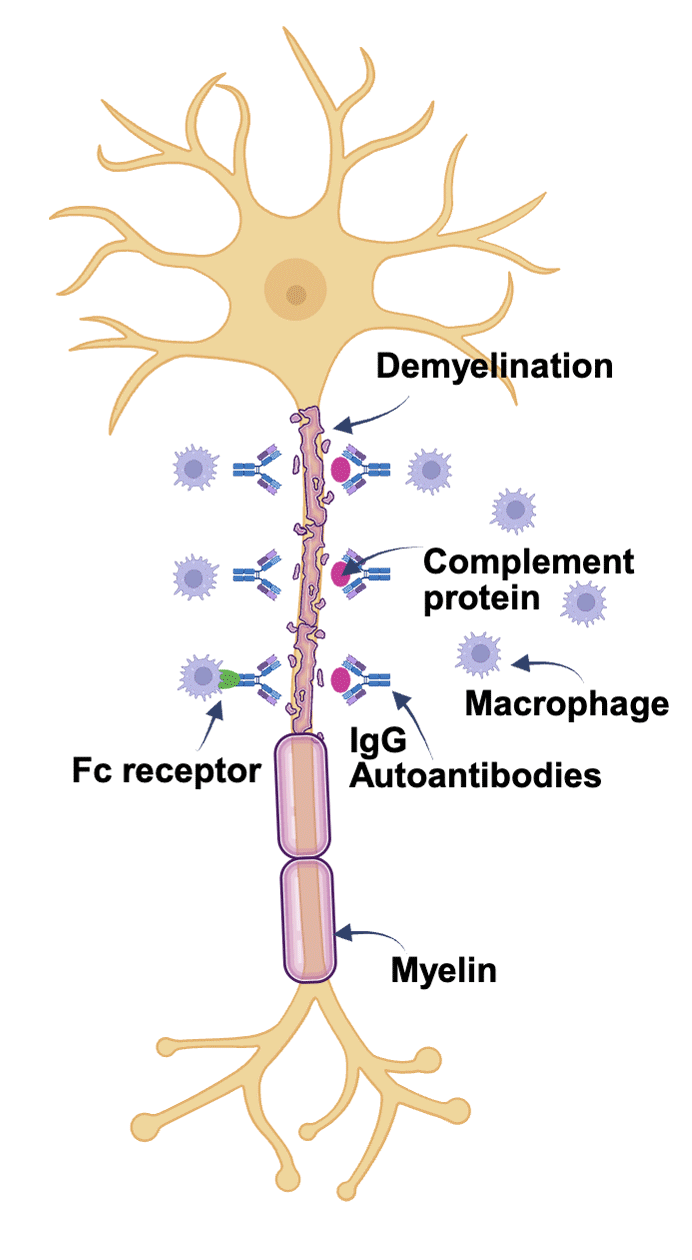
Figure created in Biorender.com, adapted from Querol et al.4

In patients with CIDP, the binding activity of IgG autoantibodies to the myelin sheath may result in demyelination, subsequent nerve damage, and symptom expression.5
When IgG anchors to the myelin sheath:
the complement pathway is activated; and
macrophages may bind to the Fc receptor and phagocytise the myelin.4,5
Burden of Disease and treatments
Symptoms
You may not see it, but many patients with CIDP continue to experience debilitating symptoms that often require burdensome treatments.2,3,6
Symptoms of CIDP worsen over�8 weeks or more, and their course may be progressive, relapsing/remitting, �or monophasic.7
Burden of CIDP disease and treatments

CIDP can significantly impact quality of life.

Even after treatment, 88% �of patients from a Dutch registry reported residual symptoms, including pain (52%) and fatigue (77%).14
Patients with CIDP are:
3x more likely to be hospitalised
2x more likely to have an ER visit
shown to have 7.5x higher medical costs15
One study reported that 44% of patients stopped working due to their symptoms, and patients expressed concerns about disease progression, dependency on others, and disease-associated financial hardships.11



88
%
44
%

IVIg, corticosteroids, and plasma exchange are considered first-line therapies for CIDP. While these treatments can be effective, they often do not lead to complete remission.13,15
There is an unmet need to improve long-term outcomes in CIDP, and more convenient treatment administration that allows patients to maintain quality of life at the highest levels for the longest period possible.14,16


The chronic nature of CIDP continues to impose significant hardships, as current treatments fall short of halting disease progression, highlighting the ongoing need for more targeted therapies that also align with the needs and priorities of patients.16
Conclusion

1. Brun S et a l. Immuno. 2022;2:118-31.
2. Van den Bergh PYK et al. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2021;26(3):242-68.
3. Broers MC et al. Neuroepidemiology. 2019;52(3-4):161-72.
4. Querol LA et al. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(3):864-73.
5. Mathey EK et al. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86(9):973-85.
6. Allen JA. Neurol Ther. 2020;9(1):43-54.
7. Cox ZC, Gwathmey KG. Clin Geriatr Med. 2021;37(2):327-45.
8. Dyck PJB, Tracy JA. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018;93(6):777-93.
9. Kuwabara S et al. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77(1):66-70.
10. Gable KL et al. Muscle Nerve. 2020;62:673-80.
11. Allen JA et al. Adv Ther. 2021;38(1):316-28.
12. Mahdi-Rogers M, Hughes RAC. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21(1):28-33.
13. Hafsteinsdottir B, Olafsson E. Eur Neurol. 2016:75(5-6):263-8.
14. Bunschoten C et al. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2019;24(3):253-9.
15. Divino V et al. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0206205.
16. Mendoza M et al. Adv Ther. 2023;40(12):5188-203.
17. Roberts A et al. Neurol Ther. 2025;14(3):1039-59.
References
CIDP: chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy; ER: emergency room; Ig: immunoglobulin; IV: intravenous.
Abbreviations

References & Abbreviations

EU-EFG-25-00013 AU-EFG-25-00007 CA-EFG-25-00016 | July 2025




Burden of CIDP disease and treatments
Many patients with �self-reported CIDP missed work or school due to treatment administration.11



A UK study found that 17% required a wheelchair at the nadir of illness 12, while a population-based study from Iceland reported 10%.13
Burden of CIDP disease and treatments




Long IV infusion times
Poor corticosteroid tolerability11
Burden of CIDP disease and treatments



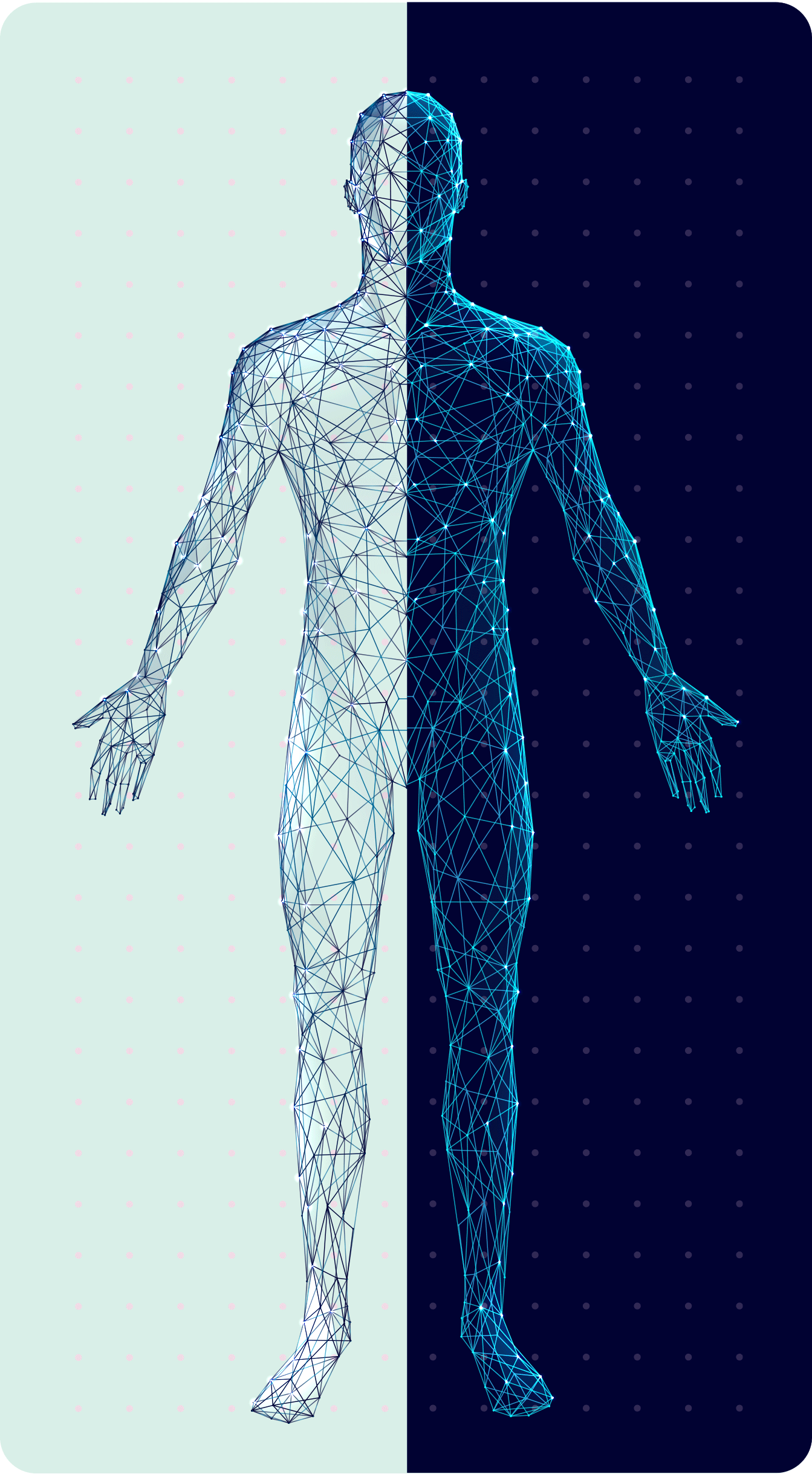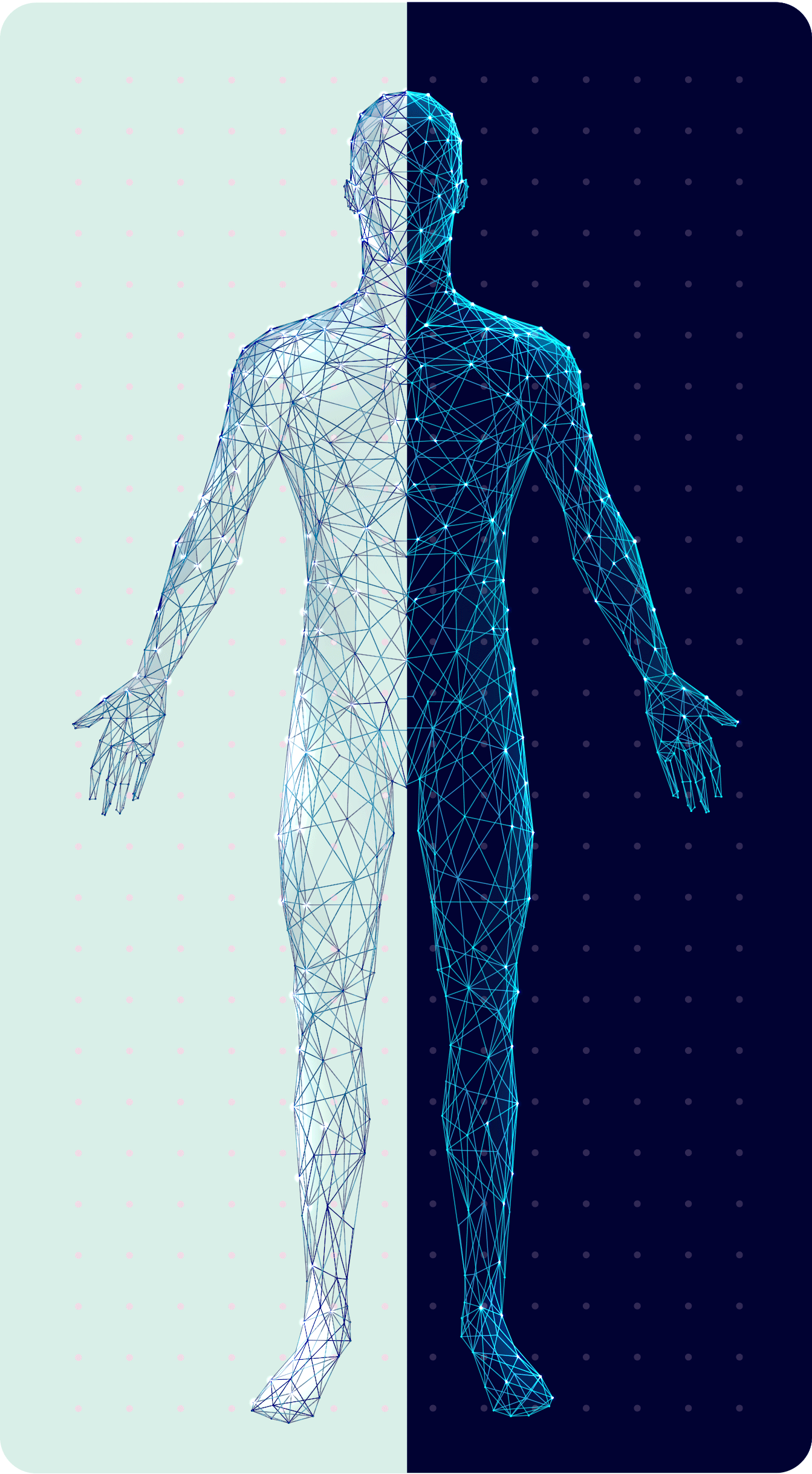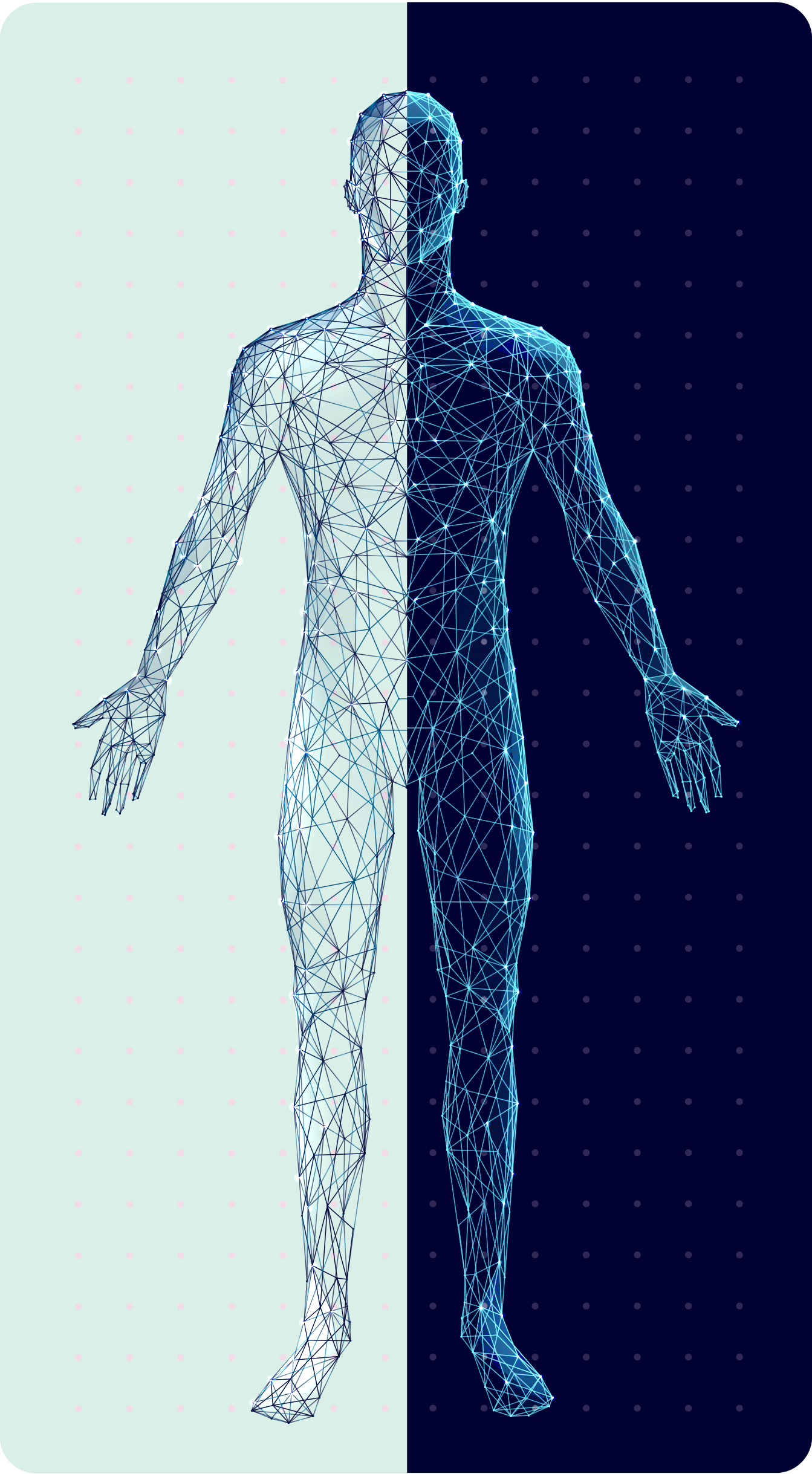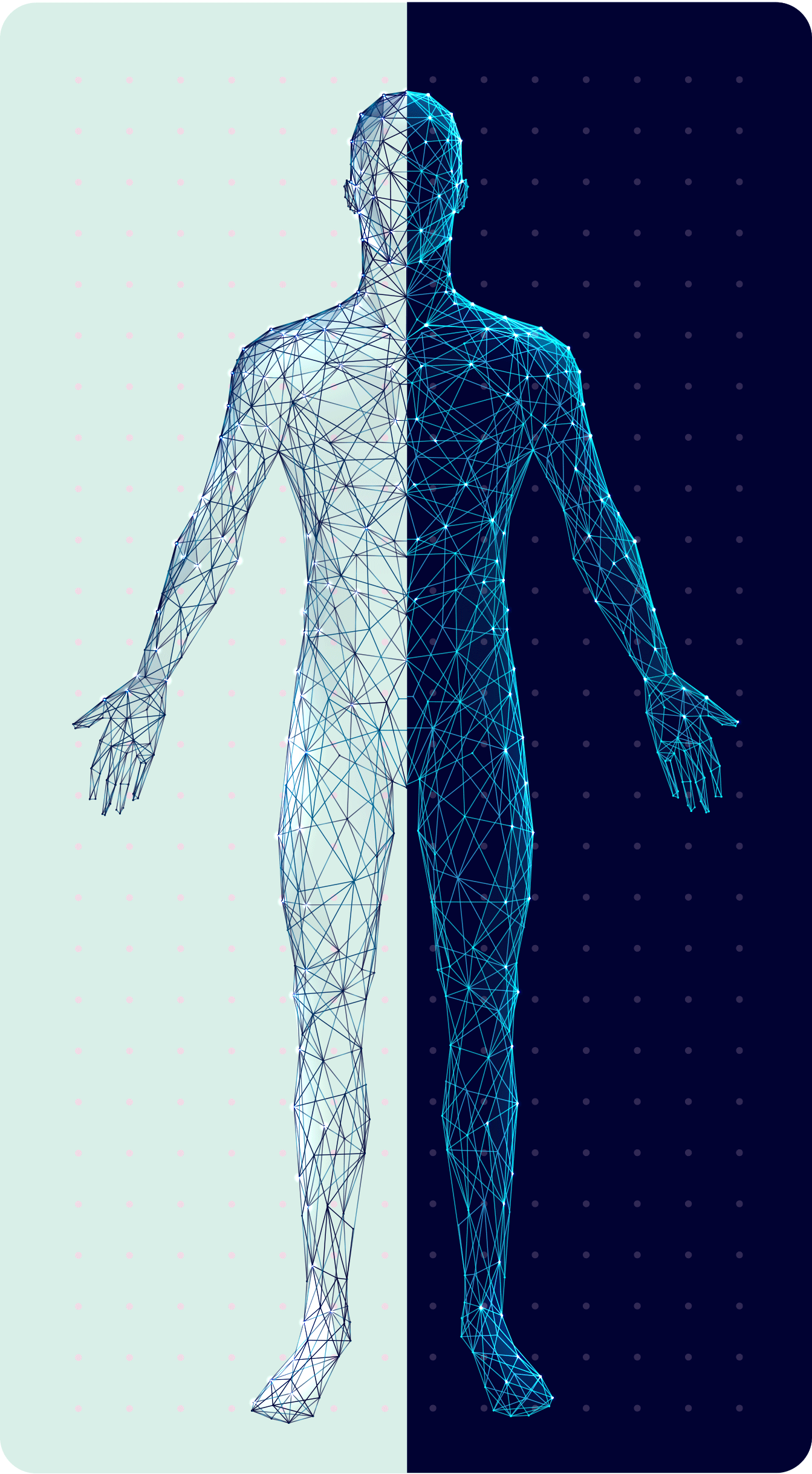
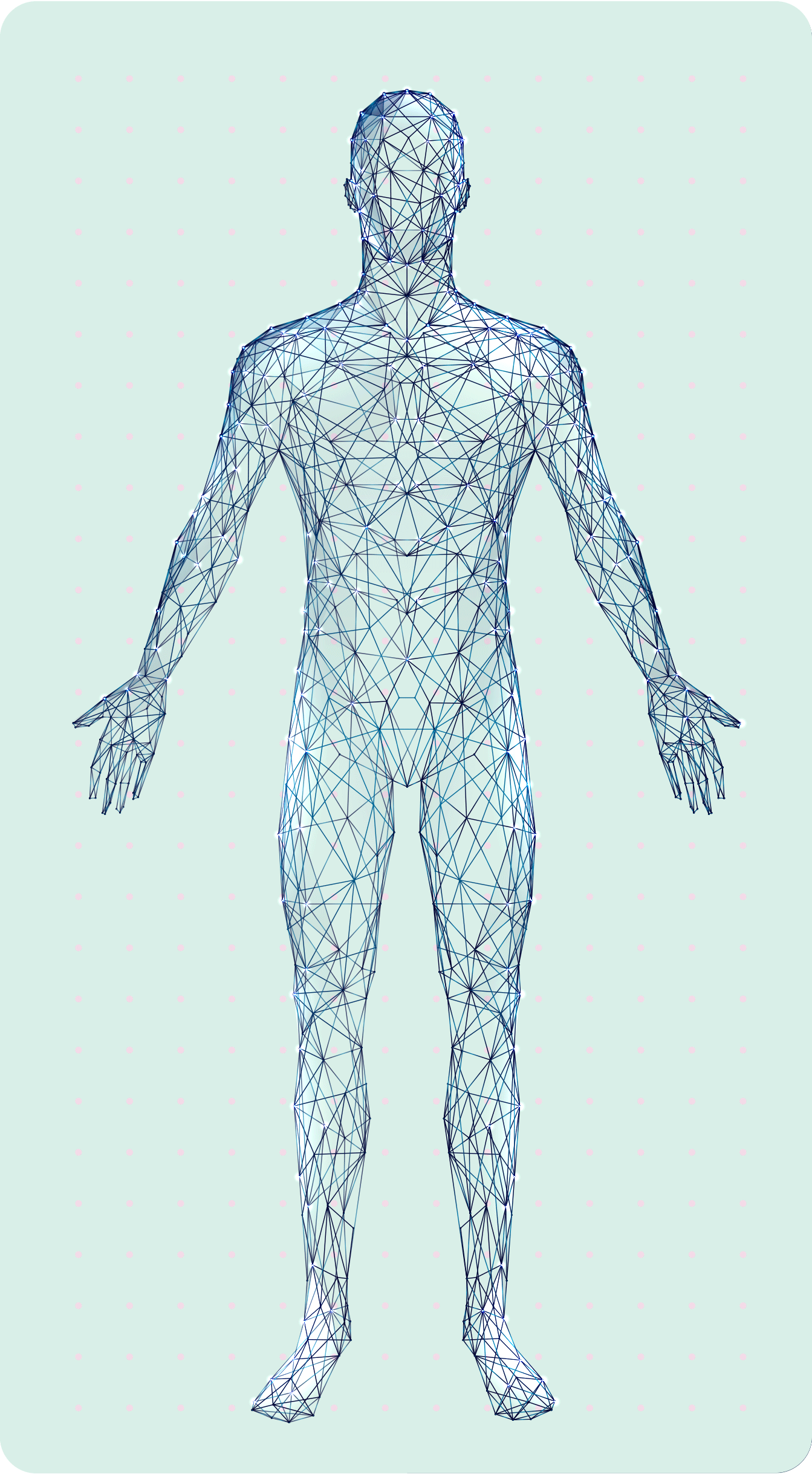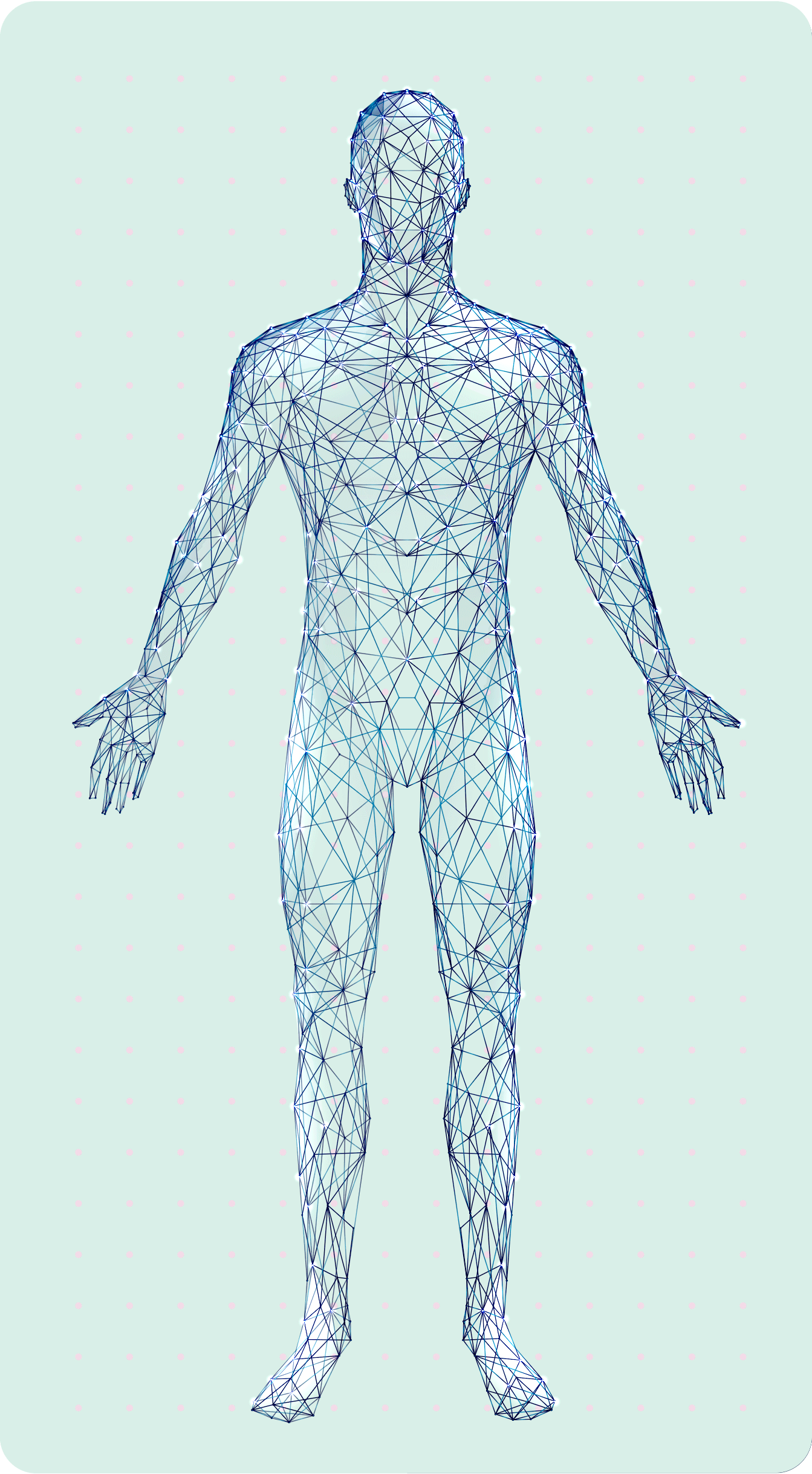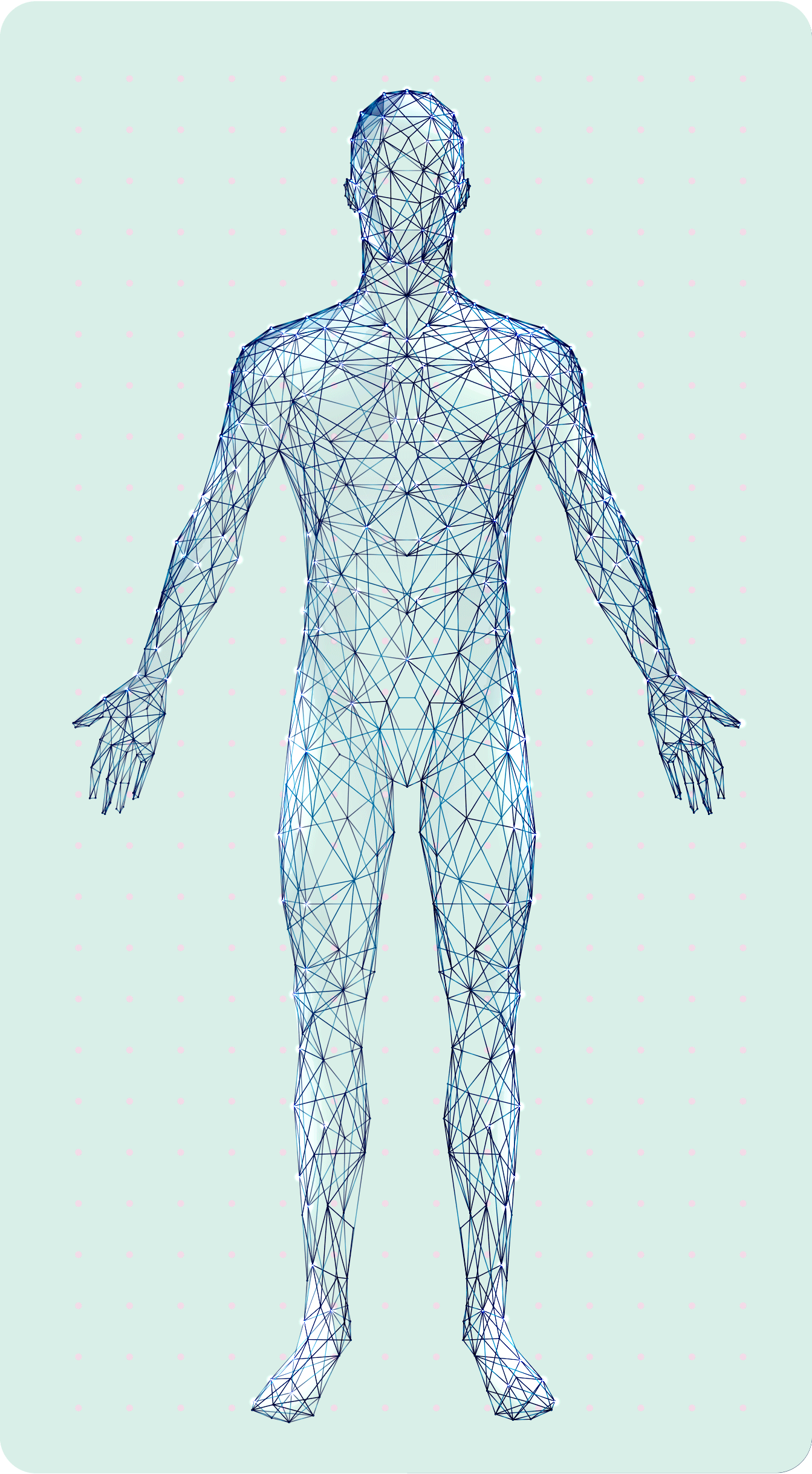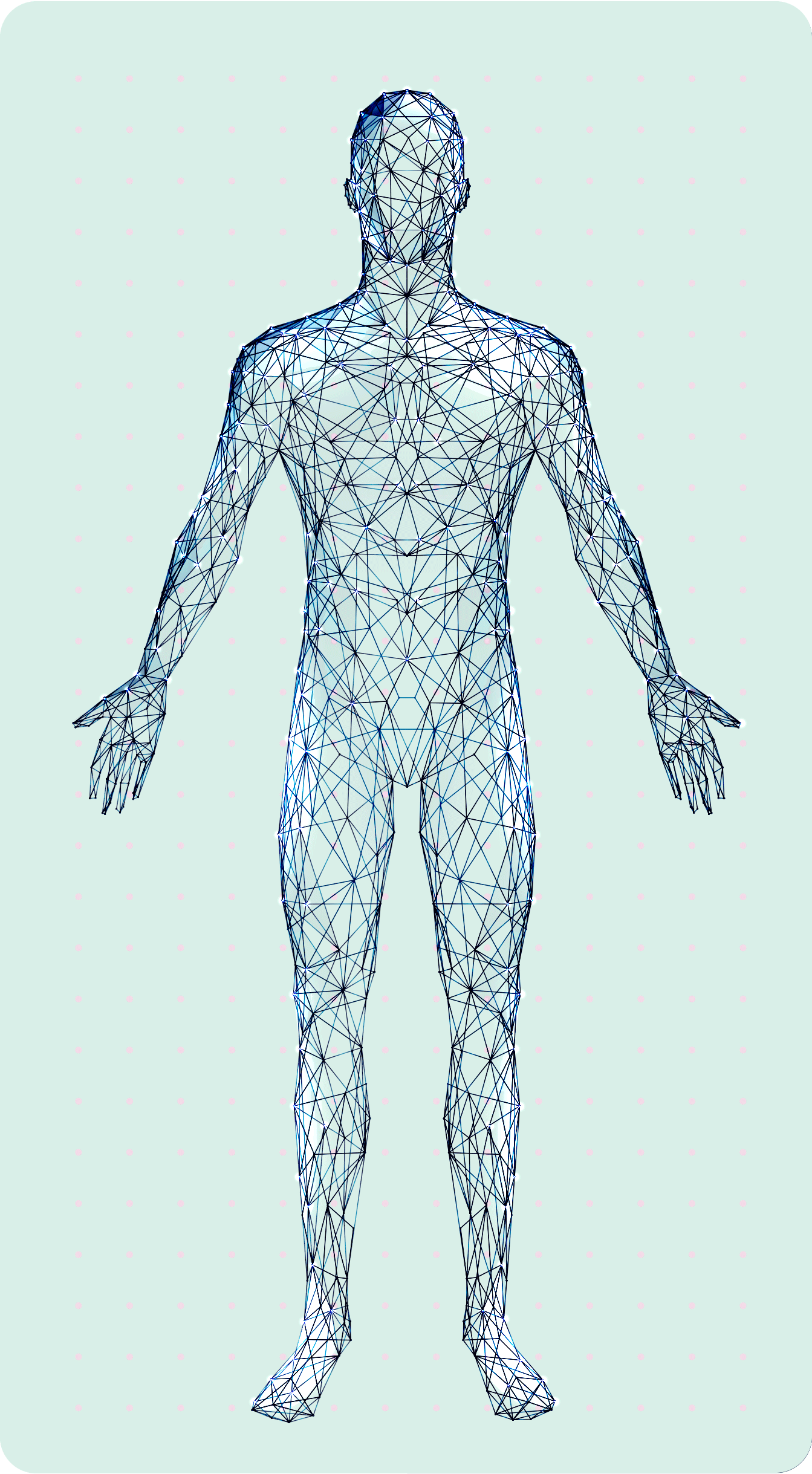
visible symptoms
1

invisible symptoms
2





invisible symptoms
2

visible symptoms
1


EXIT

visible symptoms




• Frequent tripping or falling8
• Severe disability� or inability to walk9





• Limb
weakness8

• Neuropathic� pain2

visible symptoms

invisible symptoms
2

visible symptoms
EXIT
1





• Fatigue10





• Fine motor function impairment8










This content was updated 31st July 2025 to include healthcare professionals practicing in Canada and Australia in its intended audience.
INvisible symptoms
