CD40/CD40L: A Novel Therapeutic
This infographic has been organised and funded by Sanofi

Neurology

MS is a chronic, immune-mediated, neurodegenerative disease that results in accumulation of disability over time and can have a major impact on QoL.1
Controlling both acute focal inflammation (relapses, MRI activity) and halting disability accumulation to preserve function are major treatment goals for people living with MS.1-3
INTRODUCTION

References

EU/RUXO/NP/24/0009

Target Pathway for Multiple Sclerosis



CD40/CD40L plays a critical role in the pathophysiology of MS:
Inhibition of the CD40/CD40L costimulatory pathway has the potential to modulate the activity of T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and microglia in the periphery and the CNS.7,10
This could address both acute and chronic neuroinflammation in MS which leads to disease progression and disability accumulation.4,6,10
Key Learnings


References


Abbreviations
MAT-GLB-2501633 - 4.0 - 05/2025�MAT-US-2505551 v2.0 - P Exp. Date: 05/20/2027
Naci H et al. J Med Economics. 2010;13:78-89.
Tilling K et al. Health Technol Assess. 2016;20:1-48.
Brown JWL et al. JAMA. 2019;321(2):175-87.
Elgueta R et al. Immunol Rev. 2009;229(1):152-72.
Karnell JL et al. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;141:92-103.
Pucino V et al. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2(5):e292-e301.
Aarts SABM et al. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1791.
Gerritse K et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93(6):2499-504.
Mackey MF et al. J Leukoc Biol. 1998;63(4):418-28.
Mathur RK et al. Trends Parasitol. 2006;22(3):117-22.
Ponomarev ED et al. J Immunol. 2006;176(3):1402-10.
Wu Q et al. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2021;13:11795735211050712.
Jensen J et al. Eur J Neurol. 2001;8(4):321-28.
Gerritse K et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93(6):2499-504.
Howard LM et al. J Clin Invest. 1999;103:281-90. 16.
Vermersch P et al. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2025;27(7):doi.org/10.1007/s11940-024-00818-2. 17.
Laman JD et al. J Neuroimmunol. 1998;86(1):30-45. 18.
Fadul CE et al. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021;8(6):e1096.
Lu et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:647588.
References

Abbreviations:
CD40L: CD40/CD40 ligand; CNS: central nervous system; MS: multiple sclerosis; QoL: quality of life; BBB: blood-brain barrier; TCR: T cell antigen receptor.
Medical writing assistance provided by Hannah Moir, EMJ, London, UK.




CD40/CD40L is a crucial costimulatory pathway involved in immune cell survival, maturation, proliferation, and cytokine production.4-6
It regulates both innate (macrophage, microglia, and dendritic cell) and adaptive (T and B cell) immune responses.4,5,7-10
Role of the CD40/CD40L Costimulatory Pathway in Immune Function








MHC II compleX
Macrophages
Dendritic cells
T CELLS
B CELLS
INNATE�IMMUNE CELLS
Costimulatory pathway
ADAPTIVE IMMUNE CELLS
T cell antigen receptor (TCR)

CD40L expressing immune cells

CD40�expressing cells











Microglia
Neurons
Astrocytes
Developed by Moir, H.J. Created in BioRender.com EMJ (2025)
People with MS have high levels of soluble CD40L that broadly correlates with disability.12
People with MS also have T cells that express higher levels of CD40L compared to healthy controls.13,14
CNS-infiltrating CD40L+ T cells may be key drivers of CD40-mediated inflammation in MS.15
CD40/CD40L in MS Pathophysiology4,5

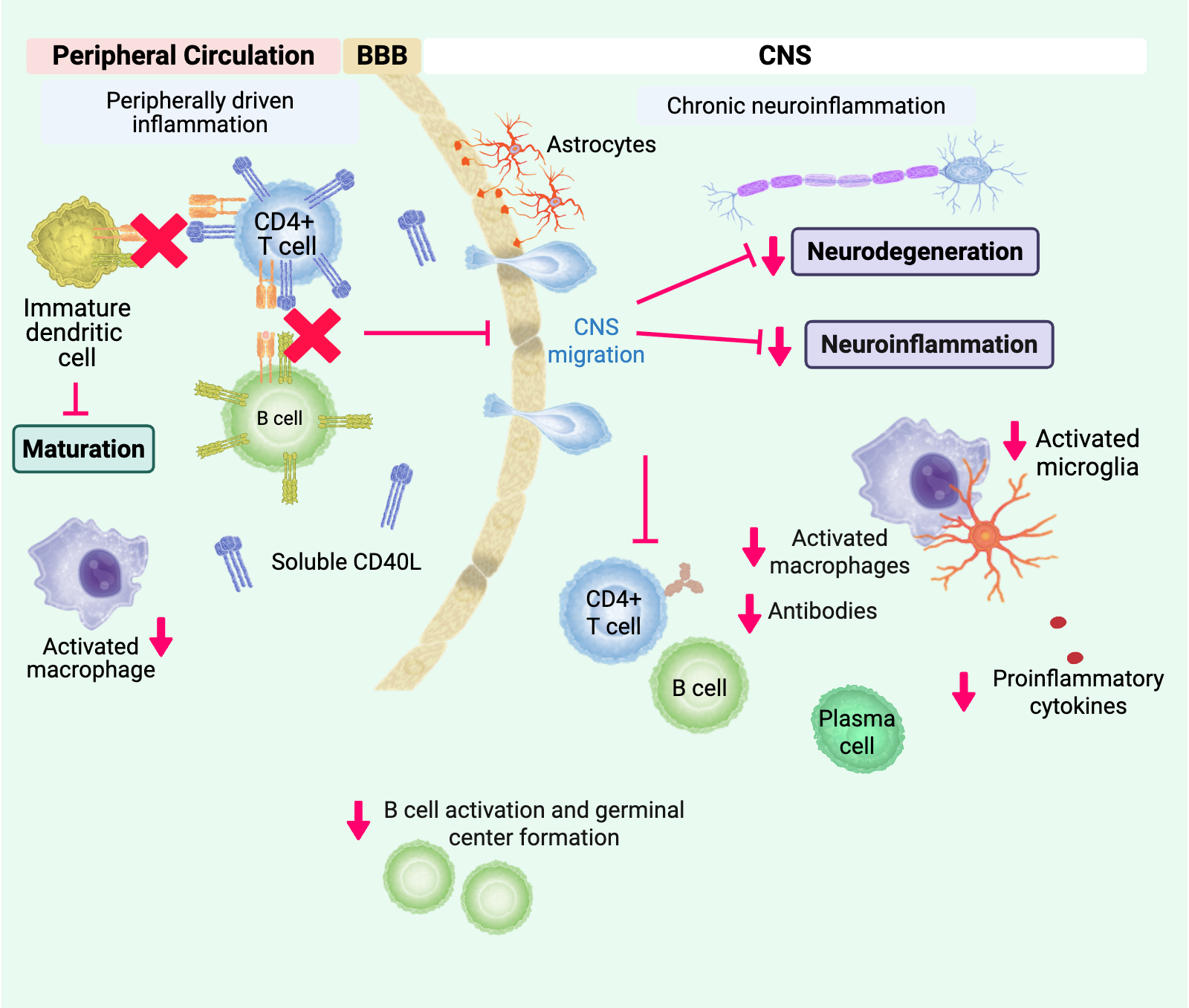
Blocking the CD40/CD40L costimulatory pathway
May modify the activation and function of T cells, B cells and innate (macrophages and dendritic cells) immune cells including reduced inflammatory cytokine production.4-8,10,17,18
May reduce CNS infiltration of CD40L+ peripheral immune cells, which prevents subsequent activation of CNS-resident immune cells that express CD40 (microglia, macrophages, astrocytes) ultimately preventing chronic neuroinflammation.5,7,8,10,19
CD40L Inhibition as a Potential Target in MS16




CD40-expressing CNS cells





CD40/CD40L co-stimulation promotes macrophage activation, antigen presentation, phagocytosis, and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion.5,7,10
CD40/CD40L co-stimulation promotes dendritic cell maturation leading to immune activation and antigen presentation4,5,7


CD40/CD40L interaction is crucial for B cell activation, proliferation, differentiation, cytokine and antibody production4,5,10



CD40/CD40L signalling is required to fully activate microglia and astrocytes for immune surveillance, cytokine and chemokine production11


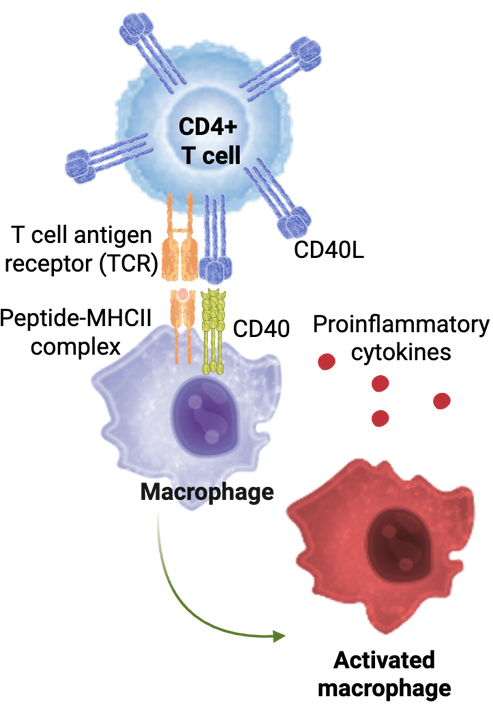
T cell antigen receptor (TCR)
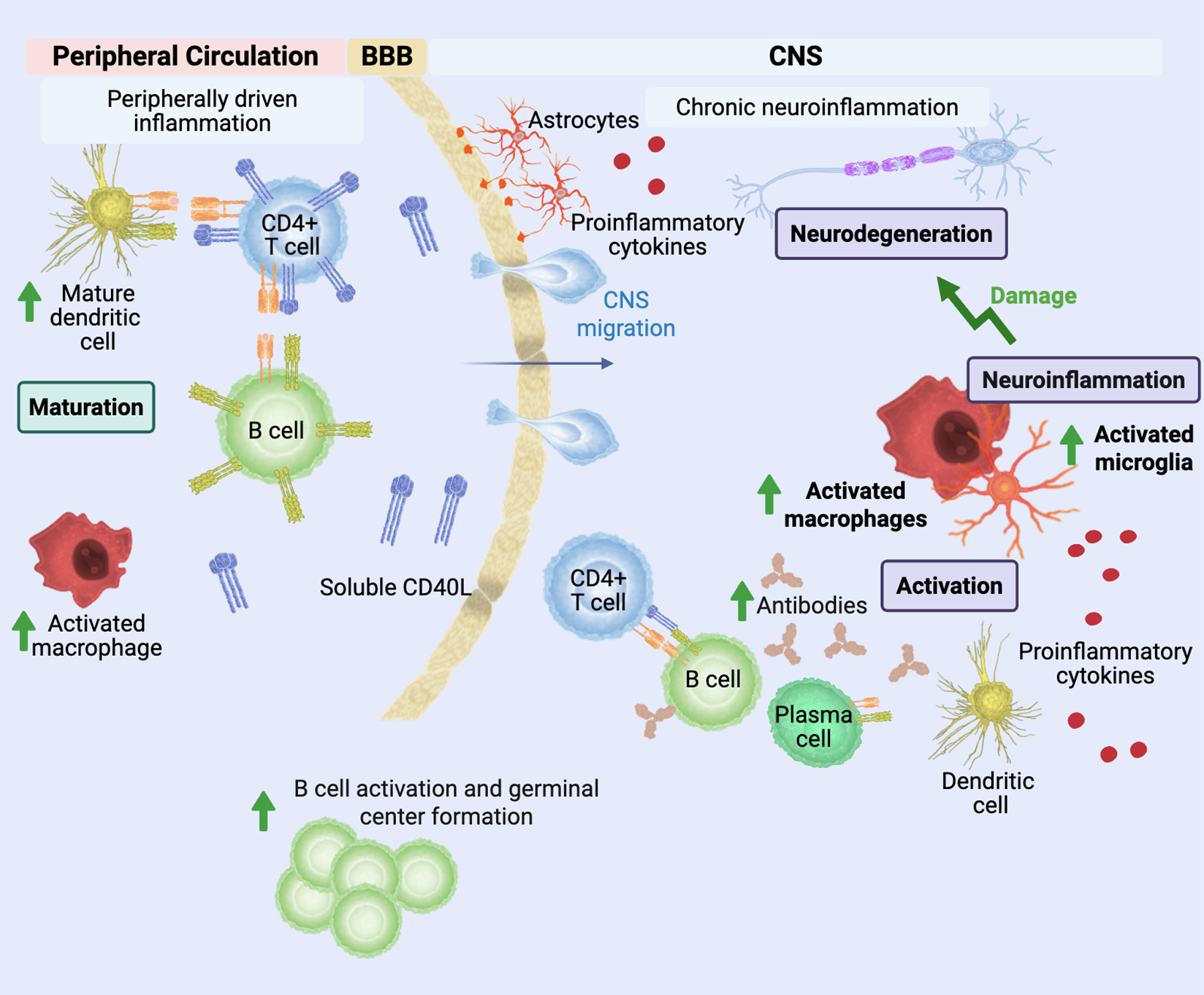






Increased CD40L+ T cells activate CNS macrophages, microglia, B cells, and plasma cells, contributing to neuroinflammation and subsequent demyelination in MS.7,17