
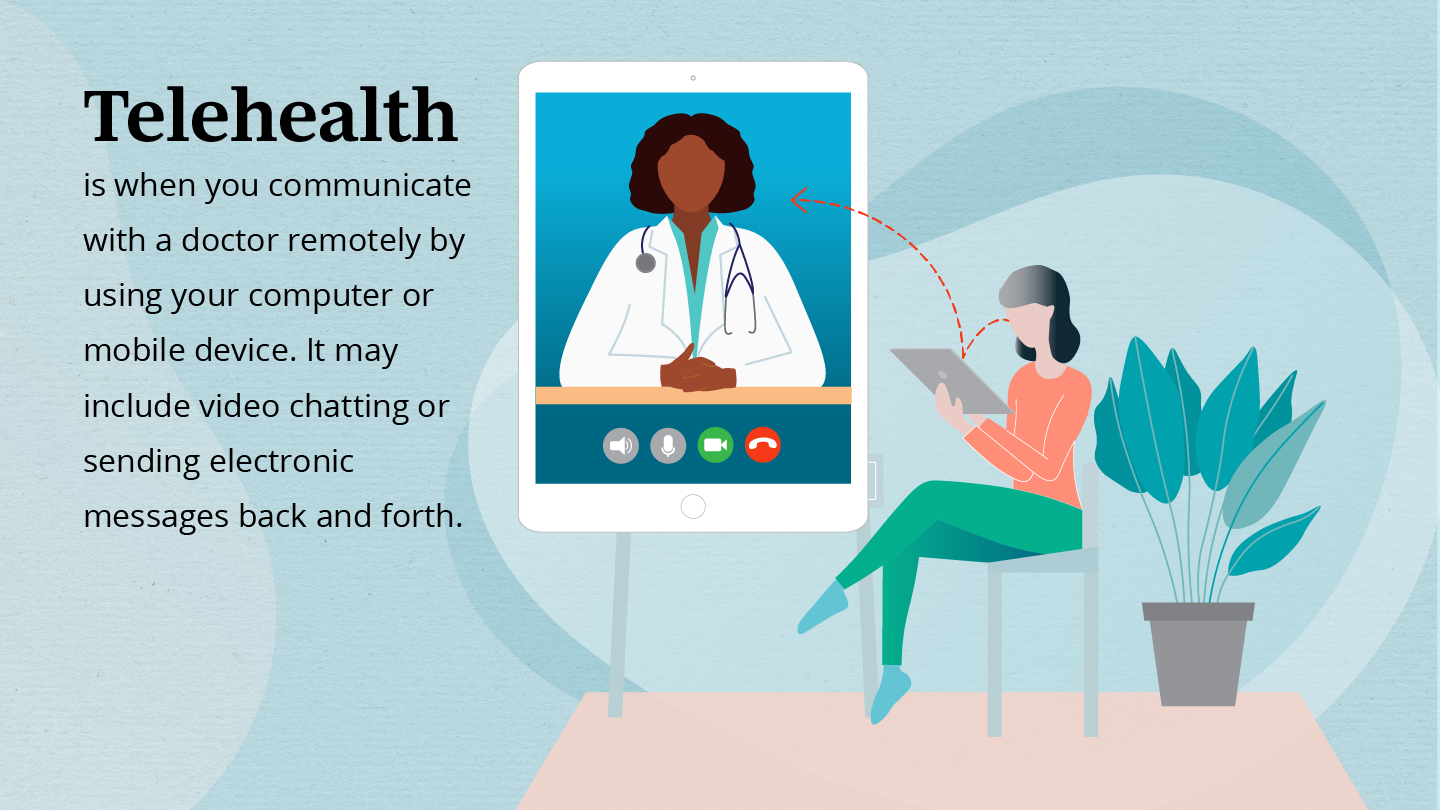
GLP-1 agonists
mimic a natural hormone in your body called glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), which is produced in the lining of the intestines.


GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1



Back
Back

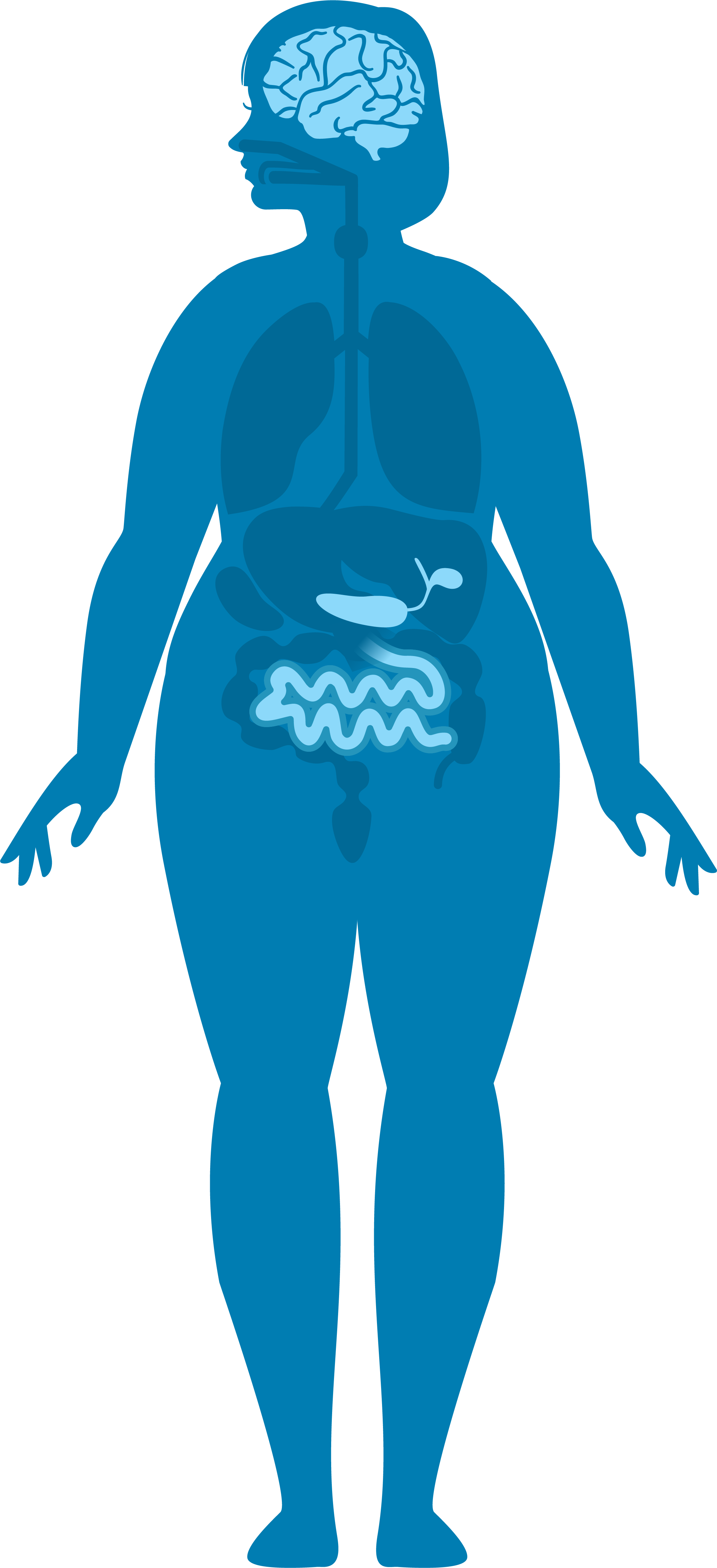
When you eat, GLP-1 triggers the pancreas to release insulin, which helps prevent spikes in blood glucose (sugar) after meals.


INSULIN

When you eat, GLP-1 triggers the pancreas to release insulin, which helps prevent spikes in blood glucose (sugar) after meals.






GLP-1 also blocks the pancreas from secreting glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar.


Back
Back

GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLUCAGON

GLP-1 also blocks the pancreas from secreting glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar.


Back




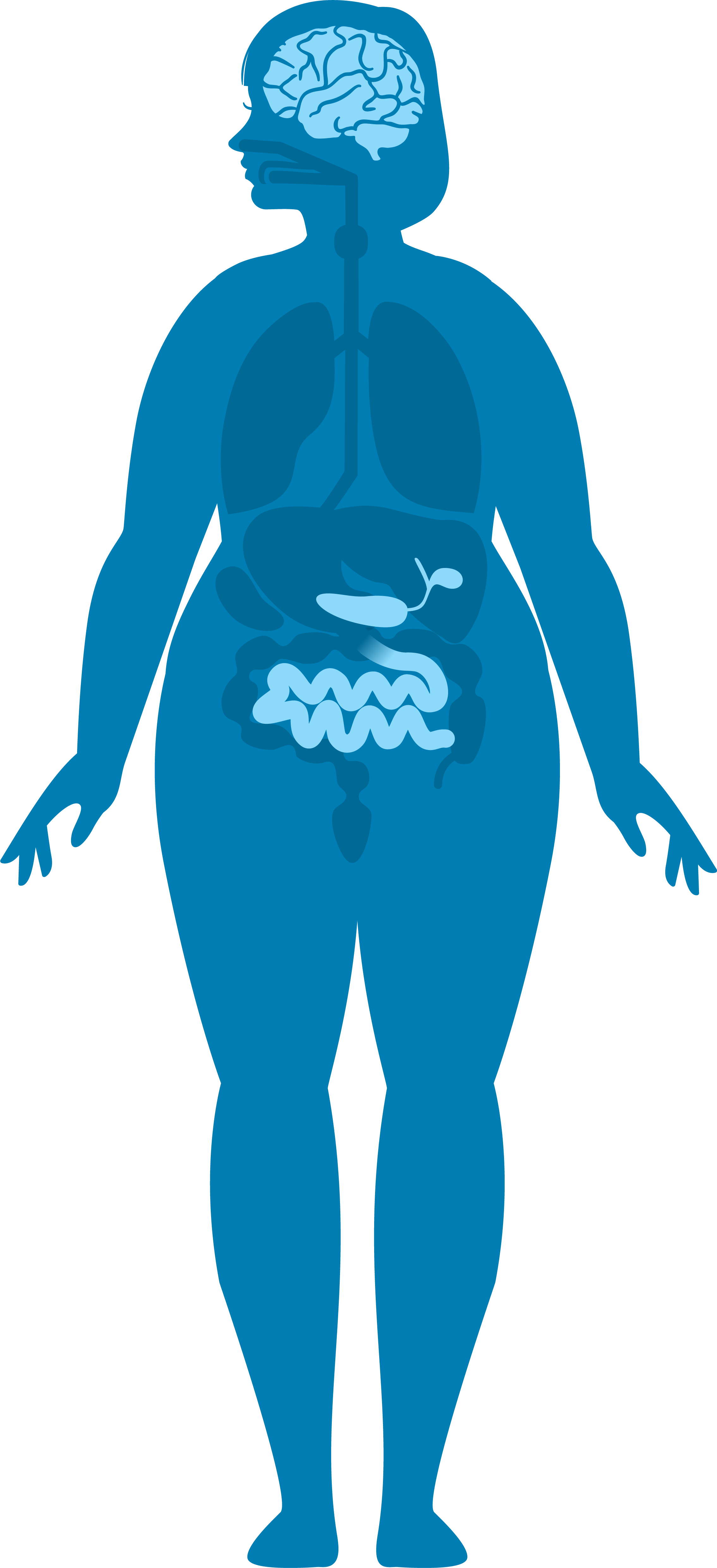
During digestion, GLP-1 slows the rate at which food empties from the stomach into the intestines, reducing how fast glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream.


Back
Back

GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1
GLP-1


During digestion, GLP-1 slows the rate at which food empties from the stomach into the intestines, reducing how fast glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream.


Back