Start Tour
Treatment guide
for migraine
presents
End Tour




CGRP therapies help block the action of CGRP, which is a protein that nerve cells produce. CGRP appears to play a role in increasing the sensitivity of nerve fibers.
People with migraine have higher than average levels of CGRP in their blood and saliva. Blocking CGRP can halve the frequency and duration of migraine symptoms, usually within 3 months after starting treatment.
Head, senses, and mood
CGRP therapy may increase the risk of certain respiratory and urinary tract infections. In rare cases, CGRP therapy may trigger a hypersensitivity immune reaction that can range from mild to severe.
Potential symptoms include skin swelling, hives, itching, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, and loss of consciousness. A severe hypersensitivity reaction requires emergency treatment.
Immune system




END TOUR





CGRP therapy may help prevent nausea and vomiting from migraine. On the other hand, CGRP therapy may sometimes cause nausea as a side effect of treatment. Other potential side effects include diarrhea, constipation, and cramps.
A person’s doctor may recommend certain lifestyle changes, dietary supplements, or medication to help manage constipation.
Gastrointestinal system
Cardiovascular system
CGRP therapy blocks the action of CGRP, which plays a role in relaxing blood vessels. Although more research is necessary, CGRP therapy might raise the risk of high blood pressure.
A person’s doctor will assess their blood pressure during regular checkups and may recommend changes to their lifestyle or treatment if their blood pressure increases.


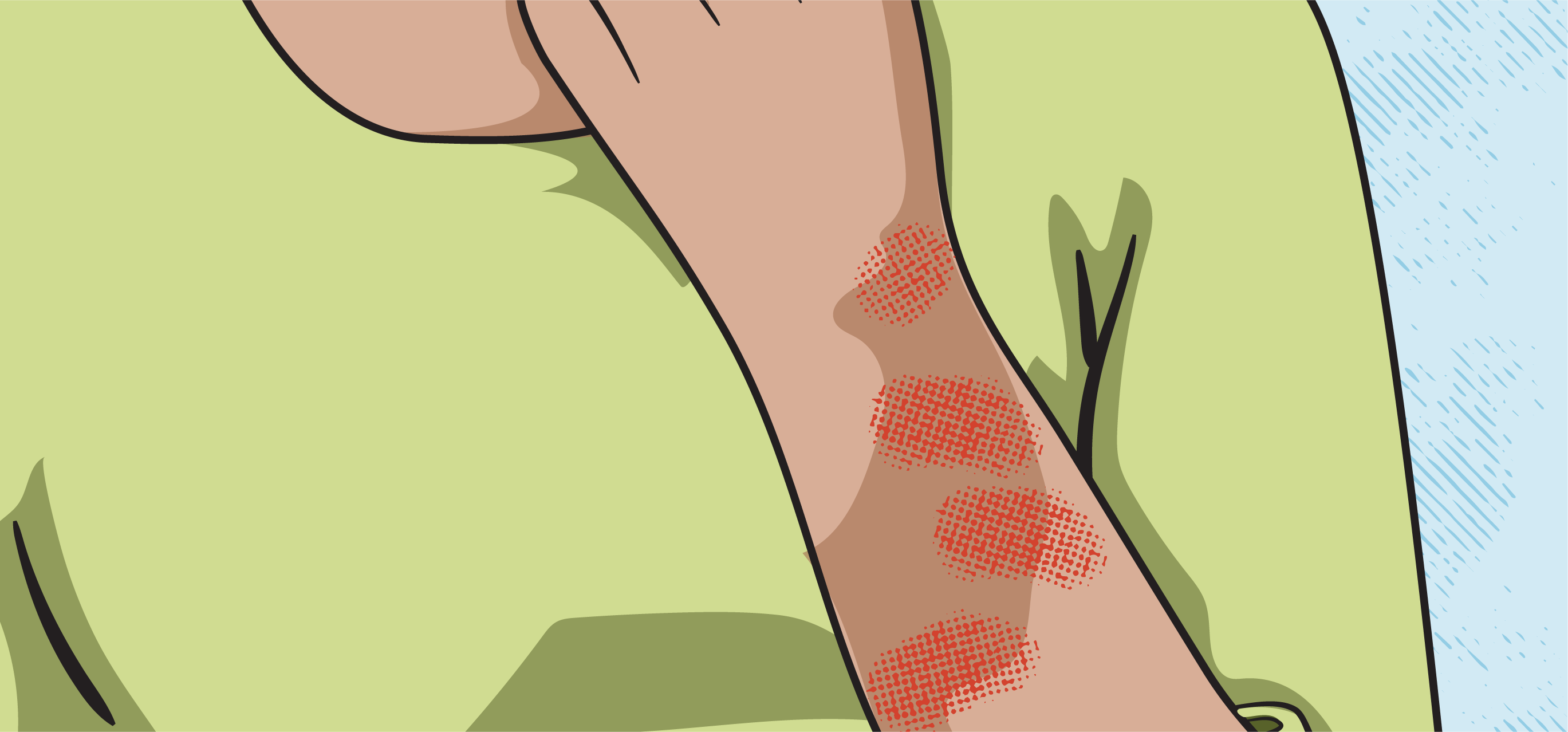
CGRP therapies for migraine prevention are injectable drugs. The most common side effect is injection site reactions, which may cause swelling, pain, or itching around the injection site.
These symptoms typically resolve on their own within a couple of days. More widespread skin swelling, facial flushing, hives, or rash may indicate a hypersensitivity immune reaction that requires treatment.
Skin
Different types of in-office or surgical options are possible, depending on the cause of dry eye symptoms.
Surgical procedures
If tears are draining too quickly from the eye, punctal plugs can be used to block the tear ducts and help keep tears on the eye longer.
Other in-office procedures can help treat dry eye, such as intense pulsed light and thermal treatments LipiFlow, iLux, or TearCare.
A procedure known as amniotic membrane transplantation can also help treat severe dry eye.
Conjunctivochalasis — especially nasally — can also cause dry eye symptoms and, at times, require surgical treatment.
Structural issues in the eye, such as loose eyelids, can also lead to dry eye. In these cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the eyelids, though this is not very common.
If necessary, permanent surgical closure of the tear ducts may be an option to help treat dry eye.
2
1





Treatment guide�for migraine








Nervous system
GRP therapy can help limit the number of days per month that a person experiences migraine headaches. It may help prevent other migraine symptoms, including hypersensitivity to light, sounds, and smells. It may also help prevent migraine aura symptoms, such as visual disturbances.
Some people may notice improvements in their mood after starting this treatment.