Historically, the discovery of just one new general-purpose technology at a time changed society. Think of the printing press in the 15th century, or electricity at the end of the 19th century.
Now, however, a whole ecosystem of general-purpose technologies is developing simultaneously. As they do so, they will interact in often unimaginable ways to create new paradigms. These technologies will transform entire industries and society – with ensuing investment themes.
Are we living through the most influential time ever? A hinge moment in history? There are those who argue that we are, as new technological discoveries are implemented faster than ever before.
A confluence of technological discoveries is opening up great potential for innovation. Quantum computing, artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, robotics, genomics and space – all are transforming our world. Indeed, today the smartphone in your pocket has 100,000 times the processing power of the rocket that landed man on the Moon 52 years ago – and technological development is accelerating ever faster…

Source: Nature
The processing speed of Google’s quantum computer, Sycamore, versus the world’s fastest supercomputer.
OUTFRONT
Arthur C. Clarke
Co-writer, screenplay, 2001: A Space Odyssey
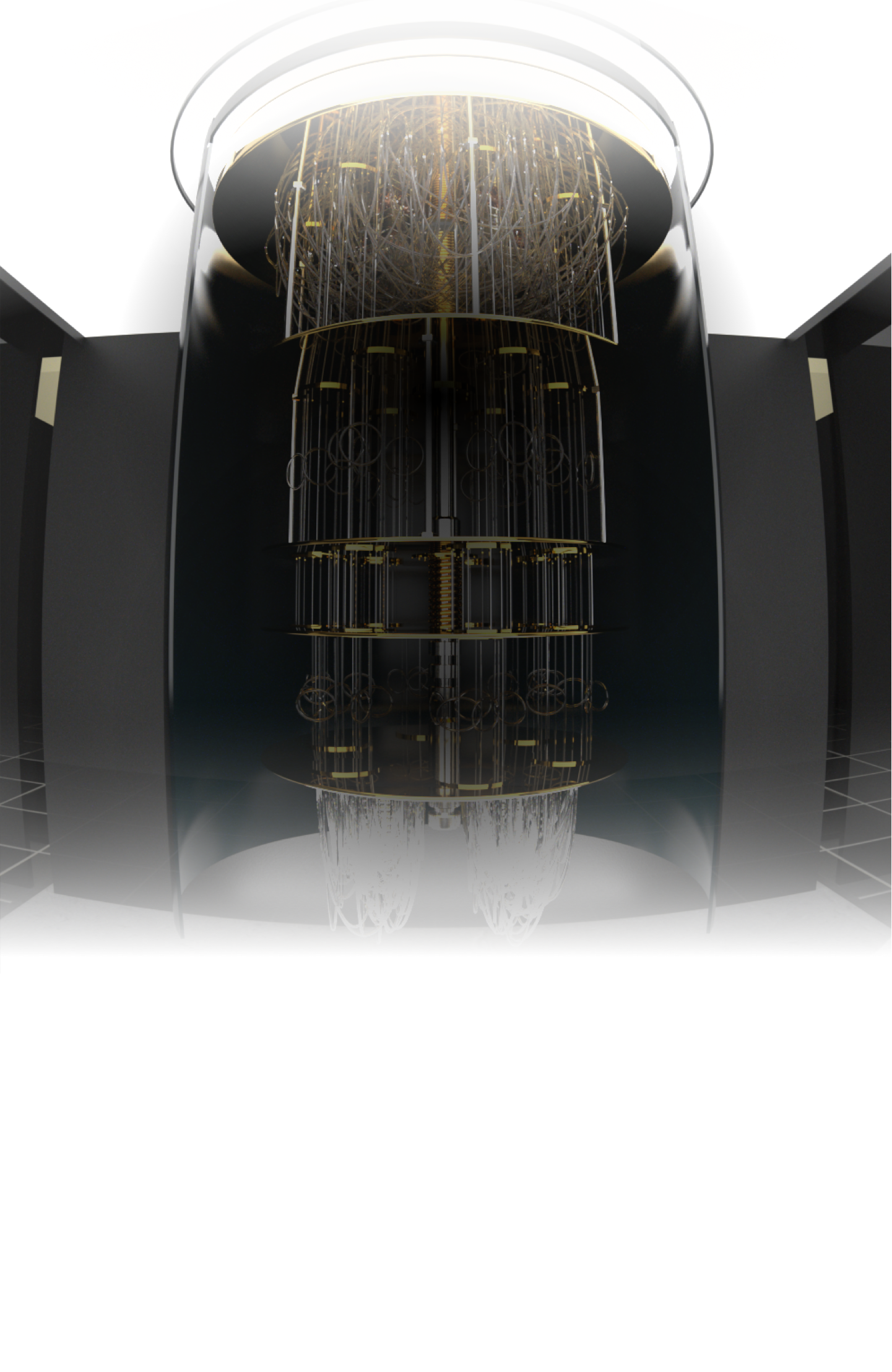
Titan Supercomputer
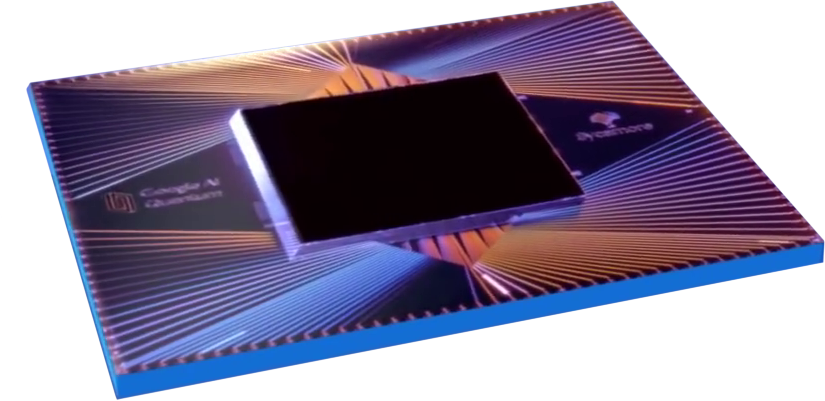
Google Sycamore

200 seconds vs 10,000 years
The time it took Google’s Quantum Computer Sycamore to perform a complex calculation versus the world’s fastest supercomputer.
By reducing computation times from years
to seconds, quantum computers have opened a door to once unthinkable possibilities.
Far faster and smarter AI.
Superconducting materials that transport electricity without losing energy.



New medicines without the need for animal testing.
Among many other things, quantum computing could help to develop:
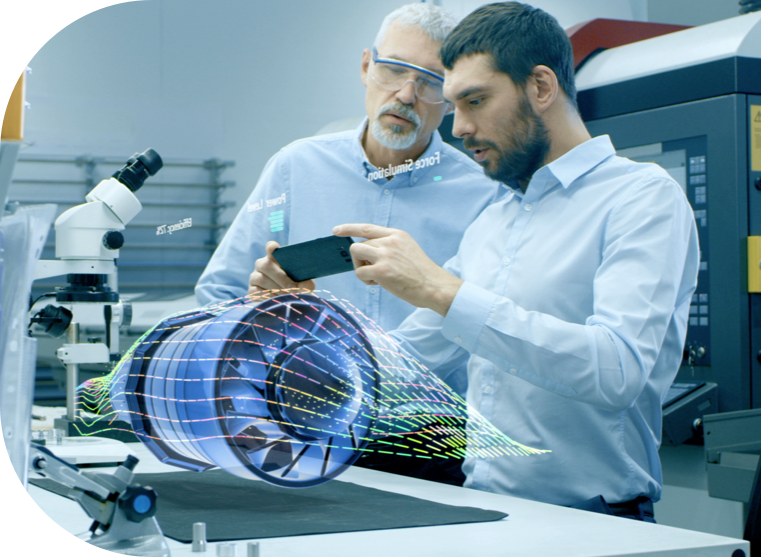
Focusing on finance, quantum computing looks set to become a critical competence – powerfully crunching data to assess likely outcomes across retail banking, capital markets, corporate finance, portfolio management and cyber encryption. But first the quantum computer’s sensitive processor must be able to operate at room temperature – currently, it is unstable unless operated in a freezer at almost absolute zero, -273.15°C.

That's equivalent to adding 1.2% a year to global GDP.
Source: McKinsey, 2018
AI is already aiding productivity across many areas of life. During the pandemic, it assisted every part of the response – from accelerating drug development, to slowing the spread through surveillance, to identifying who was most vulnerable. In finance, AI is optimizing credit decisions, trading and risk management. It’s even set to disrupt the legal profession, performing repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy.
Despite fears that AI might replace jobs, it looks more likely to reorganize the world of work, as intelligent automation frees highly-skilled workers – such as lawyers, engineers and accountants – to concentrate on cognitive tasks. AI still has a long way to go, though, before its expanding neural networks match the human brain.
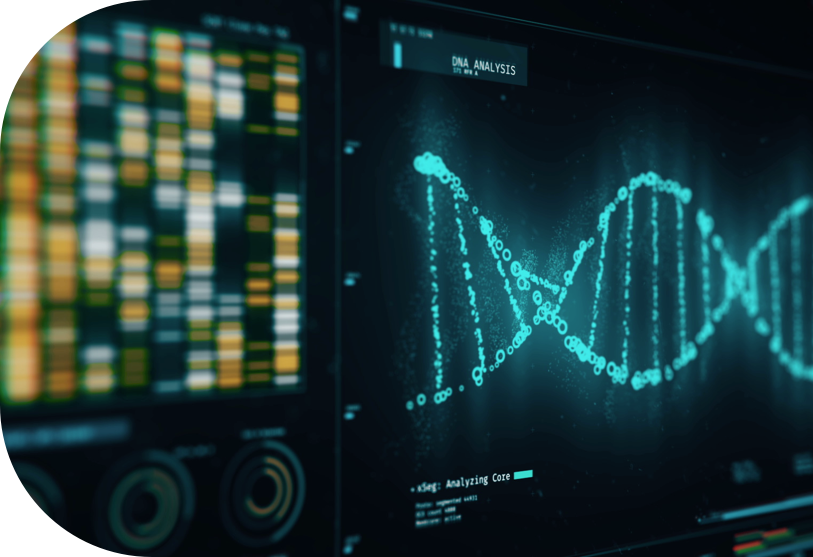


A complete human genome will improve treatments for cancers, HIV, blood disorders, muscular dystrophy, blindness, COVID-19 and many other diseases besides. And, the World Health Organization says it could help to balance out global health inequality.
Synthetic biology also raises the prospect of redesigning organisms so that they produce a useful substance – such as a medicine or fuel. For instance, new microorganisms can clean pollutants from water, soil and air, while rice can be modified to produce beta-carotene that’s rich in vitamin A and could prevent blindness in children.
What does this make possible?
TO PRINT A HOUSE
Lilongwe
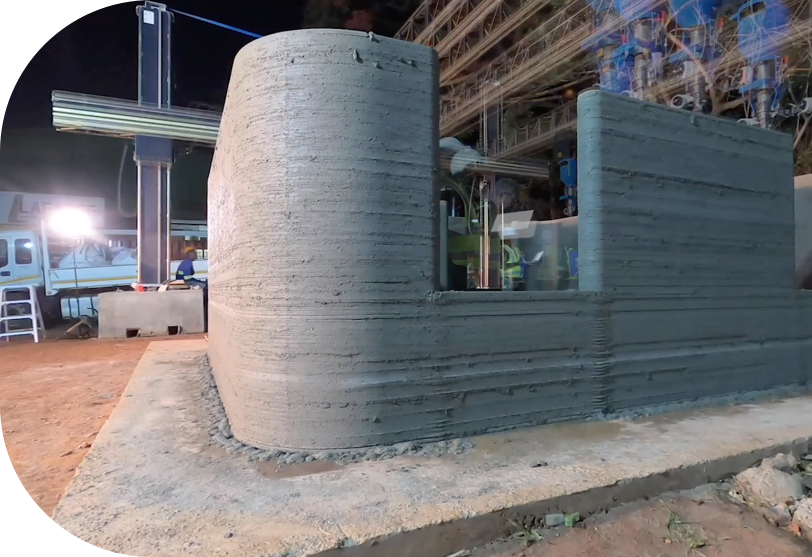
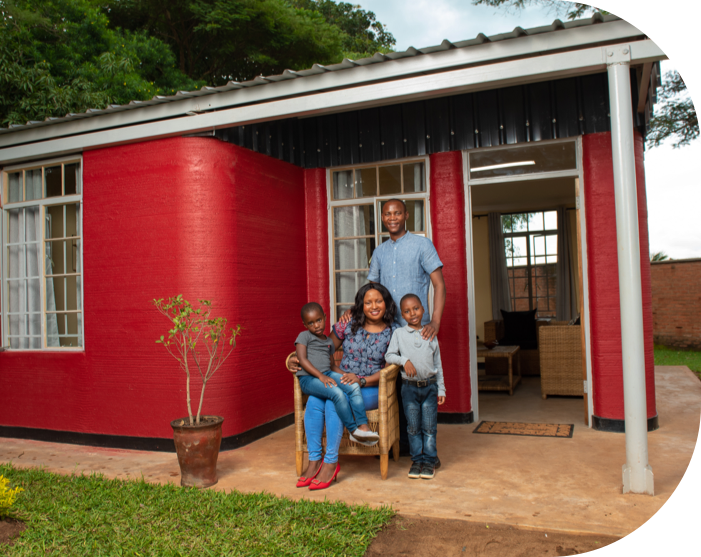
In the capital city of Malawi, a 3D printer recently built a home in just 12 hours for less than $10,000.
Video credit: 14Trees.com
Photo credit: 14Trees.com
Source: 14Trees
Within the field of bioprinting, human organs, bones and muscles can be printed.
Print-on-demand design downloads will allow consumers to print out goods, bypassing the need for stores or deliveries.



For $2,000-$3,000, a printer can be bought for the home that will print out foodstuffs from chocolate, to cheese – even meat.
From Malawi, to Dubai, to California, 3D printing is beginning to revolutionize construction, making low-cost, environmentally-friendly buildings in an industry known for its poor productivity. More widely, 3D printing is beginning to be adopted across manufacturing, used in everything from printing out entire space rockets to food.



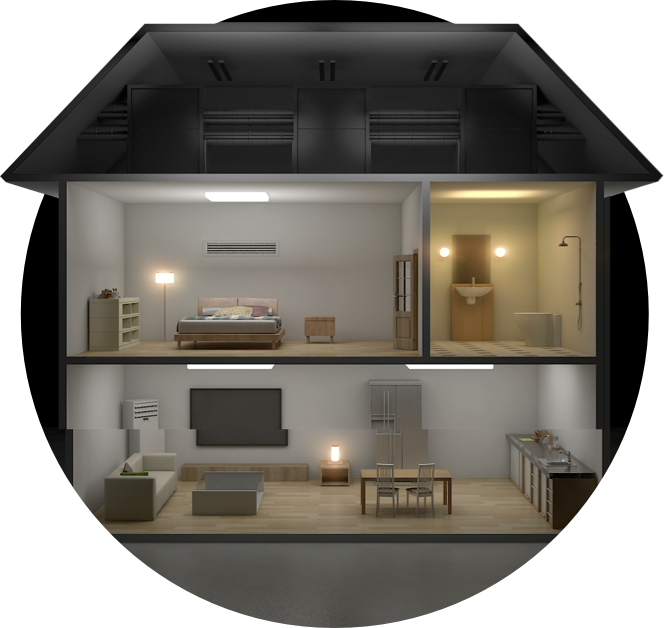
Smart houses will have everything from internet-connected sensors that monitor health to cameras that watch over pets from the office.
Behind this is next-generation 5G broadband, which delivers up to 20 gigabits of data per second and is 500% faster than 4G. This allows vast amounts of data to be processed in the “cloud”, as is vital for smart homes, cities, factories or even hospitals. In a smart hospital, cloud computing could act as a “central brain”, managing collaborative robots to deliver medicines. Across an entire smart city, 5G will allow communication between a million devices per kilometer.


63 million
Source: Swedish research firm, Berg Insight.
American homes will qualify as smart by 2022

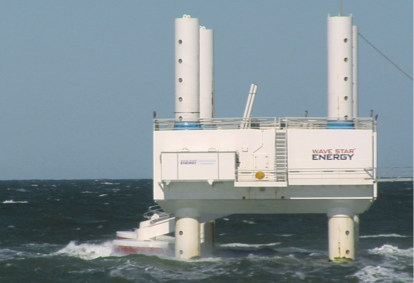
For the first time since Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi accident in 2011, nuclear generating capacity is set to grow, as safer small and advanced reactors are produced in the global race to decarbonize.
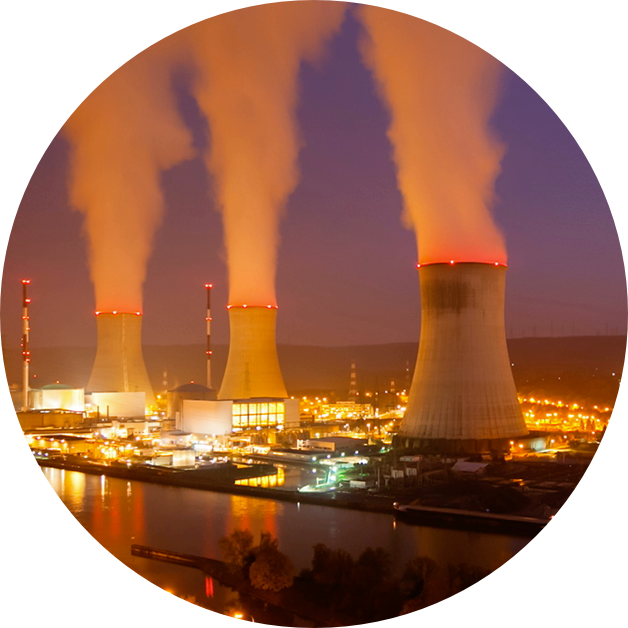

The International Energy Agency forecasts capacity will double by 2050, up from 393GW in 2020.
New technology is being developed across the energy spectrum, from solar, to wind, to hydrogen. Beyond this, ocean energy technologies have been proposed as a reliable source of renewable power – theoretically equivalent to twice current electricity consumption.
Getting on track for a 2050 net-zero carbon economy requires a surge in annual investment in clean energy projects and infrastructure to nearly $4 trillion by 2030.

792 gigawatts
nuclear generating capacity by 2050


43.8% per annum
Source: Grand View Research Inc
Forecast growth of augmented reality by 2028
Imagine a digital universe where your digital avatar interacts with others, whether playing, working or shopping.
First mooted in the cult 1992 sci-fi novel, Snow Crash, the metaverse is fast becoming the big tech companies’ vision for the future of the internet, a place where people escape reality into a virtual world. Indeed, some of the leading players are already competing to claim a part of the future metaverse, with applications for work, gaming and shopping. Beyond leisure, use of virtual reality is also growing in industry and manufacturing.
Mark Zuckerberg, chief executive of Meta (formerly known as Facebook), is staking everything on this virtual world. “Our hope is that within a decade, the metaverse will reach a billion people, host hundreds of billions of digital commerce, and support jobs for millions of creators and developers,” he said.
Yet the full vision of the metaverse may still be decades away, awaiting technical advancements, new business practices and digital currencies. Eventually, it’s likely to be far more than a new chapter for the internet – revolutionizing almost every industry.

$2 trillion
Source: IHS Markit
Forecast size of blockchain market by 2030
Forget bitcoin…
it’s the blockchain technology behind this virtual currency that looks set to turn industries upside down.
An open, distributed ledger that records transactions between two parties efficiently and permanently, blockchain has the potential to replace the contracts that enshrine trust at the heart of our economy. The ledger can be programmed to trigger transactions. As it does so, it might make many trades frictionless, cutting out middlemen like lawyers, bankers and brokers.
It’s likely to transform a wide range of industries: not just banking, but also automotive, healthcare, real estate, insurance, supply chain logistics, even agriculture. Think, for instance, of a future where you are just one among several owners of an autonomous car. Consider a financial industry with cheaper, faster settlements. In democracies, voting could even be conducted by smartphone, with instant, verifiable results. And, in healthcare, patients’ encrypted information could be shared with multiple providers. So great is the potential, that blockchain is forecast to be a $2 trillion market by 2030.

Source: Oxford Economics. How robots change the world.
Fast-paced advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning and energy storage are converging, equipping robots to take over tasks currently performed by people. Already, there are 2.25 million robots toiling globally, a number that has tripled in two decades. Trends suggest that robots will now multiply still faster, reaching 20 million by 2030, with 14 million in China alone.
This rise of robots – including drones with their myriad applications – will boost productivity and economic growth. Yet the social consequences as up to 20 million jobs are displaced could be huge.
Robots are getting smarter by the day, and the implications for lower-skilled manufacturing jobs are alarming.
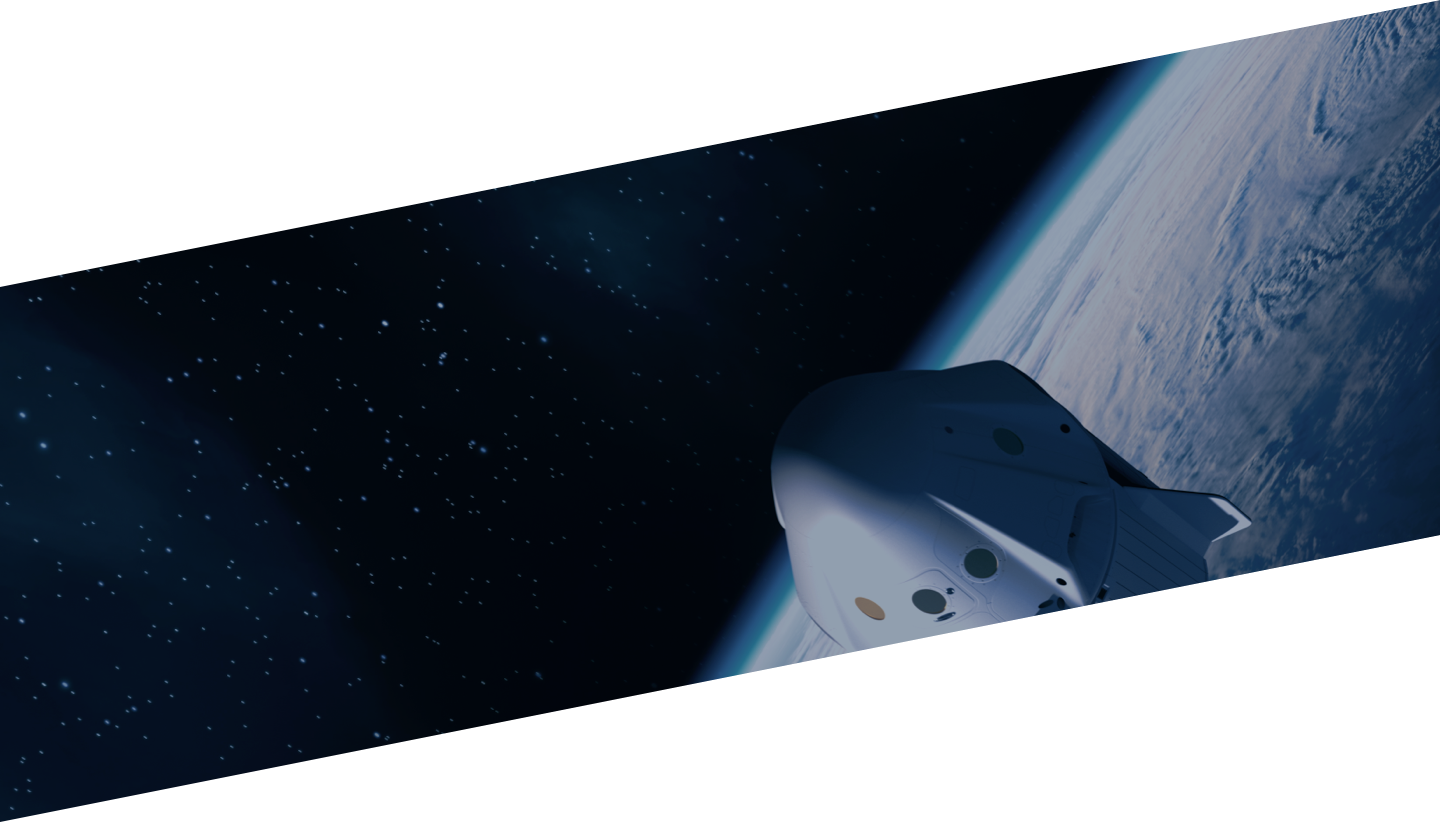
The Starship
A new SpaceX Mega rocket is meant to one day play a key role in colonizing Mars.
But long before that it will shrink the cost of access to space, with its 33 engines and power to carry 100 tons into orbit. The Falcon 9, its SpaceX predecessor, has already slashed the cost of a satellite launch by a third to $5,000 a kilogram. Starship could further lower the cost to $1,000 or even $500.
While it may be the leader, venture capital investor-backed SpaceX is far from the only private sector space company competing with the likes of NASA. Beyond the US, there were at least 160 Chinese commercial space organizations in 2020, many of them private. Today’s space companies do not just build rockets – they also own increasingly sophisticated satellites, capable of monitoring greenhouse gas emissions on Earth, tracking weather patterns and transforming internet connectivity.
Encouraged by the tumbling costs of going to space – with reusable rockets and smaller, cheaper satellites – commercial ventures are drawing record levels of funding. Total venture capital investment has accelerated sharply since the beginning of 2020 to reach new highs, according to the Seraphim SpaceTech Index, a quarterly tracker of funding deals in the sector.




The Pursuit of Outperformance
It seems likely that this is an age of Renaissance, driven by technology. In the corporate and investing sphere, it creates opportunities for the forward-looking to leapfrog competitors. More broadly, it will transform economic productivity and society in ways that are hard to imagine.
The Tech Renaissance
PRESENT
158
million times faster

10 futuristic ways that technology looks set to transform our lives
2021







2020
2019
2018
2017
2016
2015


Deal count
Deal value ($M)
5
15
10
20
30
25
60
55
50
45
40
35
0
Deal count
Deal values ($M)
200
100
300
500
400
1100
1000
900
800
700
600
Global VC Deals in Quantum Computing












Source: Pitchbook
AI to deliver a $13 trillion economic boost by 2030
2

Synthetic biology’s infinite possibilities
3
After 20 years researchers have almost finished sequencing this number of base pairs.
3.05 billion DNA base pairs
0.3% of sequence might still have errors. Includes X but not Y chromosome. Count excludes mitochondrial DNA.
Source: Nature
3D printing disrupts manufacturing
4

5G: connecting smart homes, factories and hospitals in smart cities
5
Energy’s Quest for Net Zero
6
Source: IEA
Transition in global energy supply by source to 2030 in the Net-Zero Emissions by 2050 scenario
Low emissions
Unabated combusted fossil fuels













Other renewables
Solar
Wind
Traditional use of biomass
Modern bioenergy
Hydro
Nuclear
Natural Gas
Oil
Coal

Source: IEA
2030
2020
2010
2030
2020
2010
0
EJ (exajoules)
100
200
500
400
300
Metaverse: will fantasy eclipse reality?
7

How blockchain can create the frictionless trade
8

“
Tokenization, as it evolves, should offer an opportunity to create liquidity and a low-friction trading environment for individual assets.”
Morgan Laughlin, Managing Director and Head of PGIM Real Estate (Japan)
The value of blockchain by industry vertical around the world










Healthcare
Retail and ecommerce

Advertising and media
Identity management
Supply chain and logistics
Financial
Legal and governance
Telecommunications
Government and public sector
Power and energy
Others (automotive, defense, etc.)

Source: IHS Markit
2030
2029
2028
2027
2026
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2017
0
Billions of Dollars
500
1000
2500
2000
1500





20 million robots by 2030 will change the nature of work
9

South Korea
Japan
EU
US
China
LOW ROBOT ADOPTION SCENARIO
HIGH ROBOT ADOPTION SCENARIO
Projected impact of different scenarios on annual GDP in 2030
0
–5

–10

–15

15

10

5



Source: Oxford Economics
Percentage difference from baseline

# Deals

Q2 21
Q1 21
Q4 20
Q3 20
Q2 20
Q1 20
Q4 19
Q3 19
Q2 19
Q1 19
Q4 18
Q3 18
Q2 18
$ bn
Q1 18
Seraphim trailing 12 months investment activity index (Q1 2018 = 100)
200
150

100

75

350

400

300

250



Source: Seraphim Space Tech VC Index

Space: probing new frontiers
10
Quantum computing to power a golden age
1

2020
2016
2012
2008
2004
2000
2.5
Base pairs (billions)
2.6
2.7
2.8
3.1
3.0
2.9








































































































































–7.7

11.7

–1.9

2.2

–4.3

7.5

–9.4

13.1

–8.5

9.0






























Learn More

















Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.”
“













Mark Baribeau, Head of Global Equity, Jennison Associates
As companies increasingly realize efficiencies through the adoption of big data, automation, and software, this should also drive growth in the providers of the underlying technology products and services.”
“
Source: Nature
Source: Grand View Research Inc


10. Space
9. Robots
8. Blockchain
7. AR / VR
6. Renewable Energy
5. 5G
4. 3D Printing
3. Synthetic Biology
2. Artificial Intelligence
1. Quantum Computing
INTRO
Erika Klauer, Technology Equity Portfolio Manager, Jennison Associates
Globally, 85% of all transactions are still done in cash. We see a long runway for growth in digital transactions and exciting new uses for digital wallets that go beyond everyday purchases like groceries to items such as insurance and mortgage payments.”
“
Rolls Royce Small Modular Reactor Video Credit: Rolls Royce
The Seraphim Space Index is a barometer of investment activity, showing the global volume and value of venture capital deals within the Space sector on a 12 months trailing basis, indexed against Q1 2018.


Coal fired power plant



10. Space
9. Robots
8. Blockchain
7. AR / VR
6. Renewable Energy
5. 5G
4. 3D Printing
3. Synthetic Biology
2. Artificial Intelligence
1. Quantum Computing
INTRO

Mark Baribeau, Head of Global Equity, Jennison Associates
As companies increasingly realize efficiencies through the adoption of big data, automation, and software, this should also drive growth in the providers of the underlying technology products and services.”
“
It seems likely that this is an age of Renaissance, driven by technology. In the corporate and investing sphere, it creates opportunities for the forward-looking to leapfrog competitors. More broadly, it will transform economic productivity and society in ways that are hard to imagine.
The Tech Renaissance
The Pursuit of Outperformance


Learn More
A new SpaceX Mega rocket is meant to one day play a key role in colonizing Mars.
The Starship




Space: probing new frontiers



But long before that it will shrink the cost of access to space, with its 33 engines and power to carry 100 tons into orbit. The Falcon 9, its SpaceX predecessor, has already slashed the cost of a satellite launch by a third to $5,000 a kilogram. Starship could further lower the cost to $1,000 or even $500.
While it may be the leader, venture capital investor-backed SpaceX is far from the only private sector space company competing with the likes of NASA. Beyond the US, there were at least 160 Chinese commercial space organizations in 2020, many of them private. Today’s space companies do not just build rockets – they also own increasingly sophisticated satellites, capable of monitoring greenhouse gas emissions on Earth, tracking weather patterns and transforming internet connectivity.
Encourage by the tumbling costs of going to space – with reusable rockets and smaller, cheaper satellites – commercial ventures are drawing record levels of funding. Total venture capital investment increased by 95% to $8.7 billion in the 12 months to the end of March 2021, according to the Seraphim SpaceTech Index, a quarterly tracker of funding deals in the sector.











# Deals

Seraphim trailing 12 months investment activity index (Q1 2018 = 100)
The Seraphim Space Index is a barometer of investment activity, showing the global volume and value of venture capital deals within the Space sector on a 12 months trailing basis, indexed against Q1 2018.
Source: Seraphim Space Tech VC Index
250
300
400
350
75
100
150
200
$ bn
Q1 18
Q2 18
Q3 18
Q4 18
Q1 19
Q2 19
Q3 19
Q4 19
Q1 20
Q2 20
Q3 20
Q4 20
Q1 21
Q2 21














Fast-paced advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning and energy storage are converging, equipping robots to take over tasks currently performed by people. Already, there are 2.25 million robots toiling globally, a number that has tripled in two decades. Trends suggest that robots will now multiply still faster, reaching 20 million by 2030, with 14 million in China alone.
This rise of robots – including drones with their myriad applications – will boost productivity and economic growth. Yet the social consequences as up to 20 million jobs are displaced could be huge.
Source: Oxford Economics. How robots change the world.
Robots are getting smarter by the day, and the implications for lower-skilled manufacturing jobs are alarming.



20 million robots by 2030 will change the nature of work
Percentage difference from baseline
Source: Oxford Economics
Projected impact of different scenarios on annual GDP in 2030
5
10
15
–15
–10
–5
0












US
EU
Japan
South Korea



9.0

–8.5

13.1

–9.4

7.5

–4.3

2.2

–1.9

11.7

–7.7
LOW ROBOT ADOPTION SCENARIO
HIGH ROBOT ADOPTION SCENARIO
China
Forecast growth of augmented reality by 2028
43.8% per annum
Source: Grand View Research Inc

Imagine a digital universe where your digital avatar interacts with others, whether playing, working or shopping.

First mooted in the cult 1992 sci-fi novel, Snow Crash, the metaverse is fast becoming the big tech companies’ vision for the future of the internet, a place where people escape reality into a virtual world. Indeed, some of the leading players are already competing to claim a part of the future metaverse, with applications for work, gaming and shopping. Beyond leisure, use of virtual reality is also growing in industry and manufacturing.
Mark Zuckerberg, chief executive of Meta (formerly known as Facebook), is staking everything on this virtual world. “Our hope is that within a decade, the metaverse will reach a billion people, host hundreds of billions of digital commerce, and support jobs for millions of creators and developers,” he said.
Yet the full vision of the metaverse may still be decades away, awaiting technical advancements, new business practices and digital currencies. Eventually, it’s likely to be far more than a new chapter for the internet – revolutionizing almost every industry.




Will fantasy eclipse reality?


Coal fired power plant

For the first time since Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi accident in 2011, nuclear generating capacity is set to grow, as safer small and advanced reactors are produced in the global race to decarbonize.
nuclear generating capacity by 2050
792 gigawatts
New technology is being developed across the energy spectrum, from solar, to wind, to hydrogen. Beyond this, ocean energy technologies have been proposed as a reliable source of renewable power – theoretically equivalent to twice current electricity consumption.
Getting on track for a 2050 net-zero carbon economy requires a surge in annual investment in clean energy projects and infrastructure to nearly $4 trillion by 2030.
The International Energy Agency forecasts capacity will double by 2050, up from 393GW in 2020.
Source: IEA

Rolls Royce Small Modular Reactor Video Credit: Rolls Royce

Energy’s Quest for Net Zero
Transition in global energy supply by source to 2030 in the Net-Zero Emissions by 2050 scenario
EJ (exajoules)
300
400
500
200
100
0
Source: IEA





2010
2020
2030
2010
2020
2030





































Unabated combusted fossil fuels
Low emissions
Coal
Oil
Natural Gas
Nuclear
Hydro
Modern bioenergy
Traditional use of biomass
Wind
Solar
Other renewables










American homes will qualify as smart by 2022
63 million
Source: Swedish research firm, Berg Insight.
Smart houses will have everything from internet-connected sensors that monitor health to cameras that watch over pets from the office.

Behind this is next-generation 5G broadband, which delivers up to 20 gigabits of data per second and is 500% faster than 4G. This allows vast amounts of data to be processed in the “cloud”, as is vital for smart homes, cities, factories or even hospitals. In a smart hospital, cloud computing could act as a “central brain”, managing collaborative robots to deliver medicines. Across an entire smart city, 5G will allow communication between a million devices per kilometer.




5G: connecting smart homes, factories and hospitals in smart cities
In the capital city of Malawi, a 3D printer recently built a home in just 12 hours for less than $10,000.
Lilongwe

Source: 14Trees
Photo credit: 14Trees.com
From Malawi, to Dubai, to California, 3D printing is beginning to revolutionize construction, making low-cost, environmentally-friendly buildings in an industry known for its poor productivity. More widely, 3D printing is beginning to be adopted across manufacturing, used in everything from printing out entire space rockets to food.
For $2,000-$3,000, a printer can be bought for the home that will print out foodstuffs from chocolate, to cheese – even meat.



Print-on-demand design downloads will allow consumers to print out goods, bypassing the need for stores or deliveries.
Within the field of bioprinting, human organs, bones and muscles can be printed.



3D printing disrupts manufacturing

TO PRINT A HOUSE
Video credit: 14Trees.com
What does this make possible?

A complete human genome will improve treatments for cancers, HIV, blood disorders, muscular dystrophy, blindness, COVID-19 and many other diseases besides. And, the World Health Organization says it could help to balance out global health inequality.
Synthetic biology also raises the prospect of redesigning organisms so that they produce a useful substance – such as a medicine or fuel. For instance, new microorganisms can clean pollutants from water, soil and air, while rice can be modified to produce beta-carotene that’s rich in vitamin A and could prevent blindness in children.


Synthetic biology’s infinite possibilities
Base pairs (billions)
2.9
3.0
3.1
2.8
2.7
2.6
2.5
0.3% of sequence might still have errors. Includes X but not Y chromosome. Count excludes mitochondrial DNA.
2008
2012







2000
2004







































2020
3.05 billion DNA base pairs
After 20 years researchers have almost finished sequencing this number of base pairs.
Source: Nature
2016
AI is already aiding productivity across many areas of life. During the pandemic, it assisted every part of the response – from accelerating drug development, to slowing the spread through surveillance, to identifying who was most vulnerable. In finance, AI is optimizing credit decisions, trading and risk management. It’s even set to disrupt the legal profession, performing repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy.
Despite fears that AI might replace jobs, it looks more likely to reorganize the world of work, as intelligent automation frees highly-skilled workers – such as lawyers, engineers and accountants – to concentrate on cognitive tasks. AI still has a long way to go, though, before its expanding neural networks match the human brain.
Source: McKinsey, 2018
That's equivalent to adding 1.2% a year to global GDP.




AI to deliver a $13 trillion economic boost by 2030

Google Sycamore
By reducing computation times from years to seconds, quantum computers have opened a door to once unthinkable possibilities.
The time it took Google’s Quantum Computer Sycamore to perform a complex calculation versus the world’s fastest supercomputer.
Source: Nature
Among many other things, quantum computing could help to develop:
New medicines without the need for animal testing.



Superconducting materials that transport electricity without losing energy.
Far faster and smarter AI.
Focusing on finance, quantum computing looks set to become a critical competence – powerfully crunching data to assess likely outcomes across retail banking, capital markets, corporate finance, portfolio management and cyber encryption. But first the quantum computer’s sensitive processor must be able to operate at room temperature – currently, it is unstable unless operated in a freezer at almost absolute zero, -273.15°C.

Quantum computing to power a golden age
10 futuristic ways that technology looks set to transform our lives

200 seconds vs 10,000 years
Titan Supercomputer
Deal values ($M)
600
700
800
900
1000
1100
400
500
300
100
200
0
Global VC Deals in Quantum Computing
Deal value ($M)
Deal count


Source: Pitchbook
35
40
45
50
55
60
25
30
20
10
15
5
Deal count












2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
2020







2021














+
PRESENT
Are we living through the most influential time ever? A hinge moment in history? It seems likely, as new technologies quickly fuel new ecosystems in ways that are often unimaginable.
A confluence of technological discoveries is opening up great potential for innovation. Quantum computing, artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, robotics, genomics and space – all are transforming our world. Indeed, today the smartphone in your pocket has 100,000 times the processing power of the rocket that landed man on the Moon 52 years ago – and technological development is accelerating ever faster…
Historically, the discovery of just one new general-purpose technology at a time changed society. Think of the printing press in the 15th century, or electricity at the end of the 19th century.
Now, however, a whole ecosystem of general-purpose technologies is developing simultaneously. As they do so, they will interact in often unimaginable ways to create new paradigms. These technologies will transform entire industries and society – with ensuing investment themes.
Arthur C. Clarke
Co-writer, screenplay, 2001: A Space Odyssey
Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic.”
“



Transformational Technologies Powering the 21 Century
st
OUTFRONT
The processing speed of Google’s quantum computer, Sycamore, versus the world’s fastest supercomputer.
Source: Nature
Morgan Laughlin,
Managing Director and Head of PGIM Real Estate (Japan)
Tokenization, as it evolves, should offer an opportunity to create liquidity and a low-friction trading environment for individual assets.”
“

The value of blockchain by industry vertical around the world
1500
2000
2500
1000
500
0
































































































































































2021
2022
2023
2024
2025
2026
2027
2028
2029
2030
2017
2018
2019
2020
In Billions of Dollars
Others (automotive, defense, etc.)

Power and energy

Government and public sector

Telecommunications

Legal and governance

Financial

Supply chain and logistics

Identity management

Advertising and media

Retail and ecommerce

Healthcare

Source: IHS Markit
Forecast size of blockchain market by 2030
$2 trillion
Source: IHS Markit
Erika Klauer, Technology Equity Portfolio Manager, Jennison Associates
Globally, 85% of all transactions are still done in cash. We see a long runway for growth in digital transactions and exciting new uses for digital wallets that go beyond everyday purchases like groceries to items such as insurance and mortgage payments.”
“

it’s the blockchain technology behind this virtual currency that looks set to turn industries upside down.
Forget bitcoin…
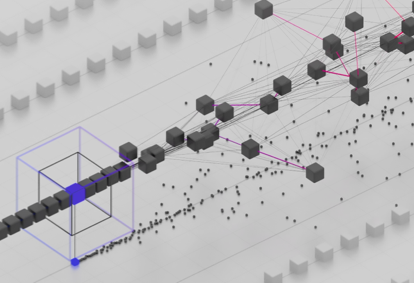
An open, distributed ledger that records transactions between two parties efficiently and permanently, blockchain has the potential to replace the contracts that enshrine trust at the heart of our economy. The ledger can be programmed to trigger transactions. As it does so, it might make many trades frictionless, cutting out middlemen like lawyers, bankers and brokers.
It’s likely to transform a wide range of industries: not just banking, but also automotive, healthcare, real estate, insurance, supply chain logistics, even agriculture. Think, for instance, of a future where you are just one among several owners of an autonomous car. Consider a financial industry with cheaper, faster settlements. In democracies, voting could even be conducted by smartphone, with instant, verifiable results. And, in healthcare, patients’ encrypted information could be shared with multiple providers. So great is the potential, that blockchain is forecast to be a $2 trillion market by 2030.




How blockchain
can create
the frictionless trade