EXPLORE Sources of Electricity
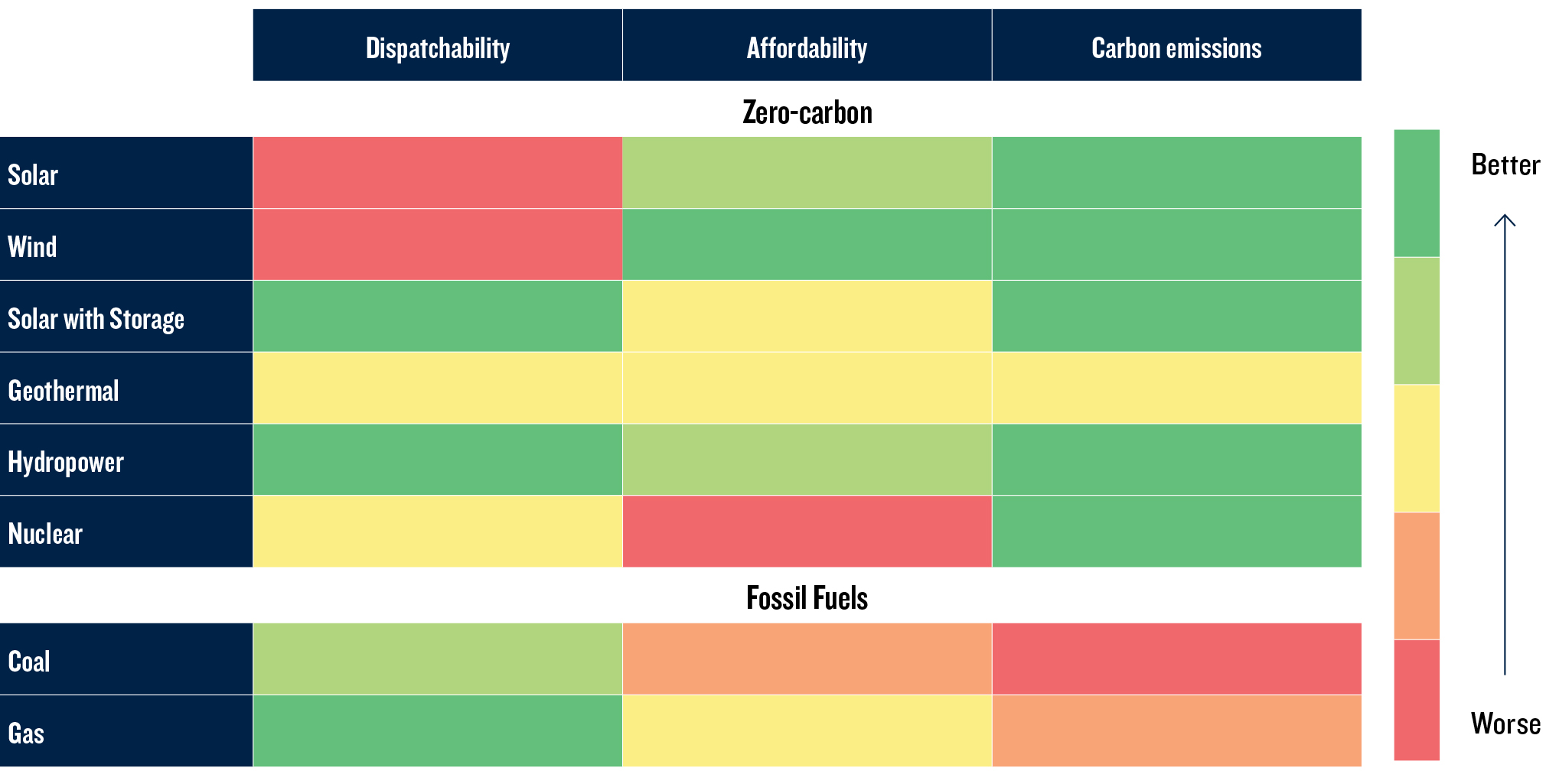
Carbon emissions
Dispatchability
Affordability
Carbon emissions
Affordability
Dispatchability
Wages
Dependable energy is not just critical for economic development, it is considered by most countries to be an essential aspect of national security.
Electricity generation still relies on fossil fuels
Share of global energy sources in electricity generation
Source: PGIM Thematic Research, Ember and Pinto, et al; 2023. March 2024.
Tech and Demographics
There are multiple economic and political reasons for the continued significance of fossil fuels, but three factors are often underappreciated in discussions on the pace of the energy transition:
Renewables have become the cost-effective way of generating electricity
Unsubsidized levelized cost of energy, price per megawatt (2023)
Note: LCOE has its limitations. For example, it does not account for the additional cost of power storage for intermittent sources to smooth out the fluctuations in their production. But even after adding the cost of firming intermittency – such as the cost of power storage or the need to supplement these renewable sources with dispatchable gas-powered plants – renewable sources remain cost-efficient in most cases – especially compared to nuclear and coal-powered plants.Source: PGIM Thematic Research, Lazard and International Energy Agency. March 2024.
Employment outlook of future leading and lagging industries in Europe
Labor Shortages
Electrification is a critical component of this decarbonization transition for two reasons:
BY REGION

Data as of August 2023.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Dispatchability refers to the ability to generate power when it is needed, i.e., how easily power production can be turned up or down to meet variations in demand.
Most renewables – especially solar and wind – are intermittent, creating new infrastructure needs and challenges.
Government support of renewables has attracted private capital, accelerating technological advancements that now make wind and solar among the most cost-efficient energy sources.
Renewable power projects generate electricity at a relatively low levelized cost of energy (LCOE) – that is, the total cost of power generation over the lifetime of the asset.
Energy – both its production and consumption – accounts for roughly 75% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
Renewable sources – once manufactured and in place – can generate electricity with no additional GHG emissions.
Regardless of how long it takes, reducing carbon emissions will remain an enduring feature of the energy landscape for decades, even as fossil fuels remain a key source for the foreseeable future.
All sources of electricity offer different tradeoffs
Increase in primary sources’ share of global energy consumption
Note: Affordability is measured by the levelized cost of energy and carbon-emissions captures emissions per BTU.
Source: PGIM Thematic Research, Lazard, International Energy Agency and US Energy Information Administration. March 2024.











Fossil Fuels
Zero-carbon