Q2 2022
Market Update
& Outlook
Report

Tap into valuable market insights
What should you expect when it comes to the transportation market this year? Will pandemic disruptions, tight capacity, inventory shortages and uncertainty continue? Or is there light at the end of the tunnel? Discover data-backed intelligence and recommended actions for North American and European shippers to advance logistics strategies in our Q2 2022 Market Update & Outlook Report.


Download the report to access the latest trends impacting supply chain leaders




Preview the Report
Keep scrolling for key highlights and to
download the full report

Cost and capacity pressures to remain through the end of the year
Scroll to the right to see insights on rates, supply, demand, labor and policy.

Rates
- Contract rates remain elevated and have not yet dropped due to recent spot
market fall.
- Spot rates and volumes have dropped sharply over the last 30 days.
- There is continued pressure on incumbent carrier pricing, but carriers are active to protect key lanes.
- Fuel and inflation are adding pressure to the carrier cost model, which is
impacting rates.
- First tender accept is showing significant improvement.
Supply

- New Class 8 orders are dropping and prices continue to increase to over $80K.
- The Drug and Alcohol database is making a larger impact than anticipated as
drivers exit and are not returning.
- There is still a bottleneck around recruiting, training and onboarding drivers.
- Fewer drivers are willing to work in teams, impacting team capacity.
- Lead time for new trucks is starting to increase again as OEM’s manage
backlogs.
- The supply of truck components is increasing but still impacting new builds.
- U.S. insurance cost continues to rise resulting in a significant impact to carriers
(mostly niche and regional carriers).
Demand

- Demand is still strong in some industries; however, post-COVID scenarios are
driving slowing demand in others.
- Realignment of industry level inventory levels is creating significant and
combined shortage/overage conditions.
- The ISM PMI index is still north of 50 which indicates strong, but slightly weaker
economic conditions.
- RFP remains on track with many shippers finalizing networks and new Q2 bids
going to market.
- Customers have largely stayed with historical RFP cycles and terms.
- Shippers have largely stayed with 1-year terms on RFP’s but are open to
pre-negotiation and different terms with core partners.
Labor

- There is a driver shortage on the asset side.
- Many drivers have left the industry permanently due to COVID-19.
- Carriers are offering additional pay for drivers to relocate to areas where
capacity is needed.
- Driver turnover is increasing as employed drivers chase higher pay
and signing bonuses.
- There is noticeable shift in long-haul driver base to short-haul for more desirable
work for drivers.
- Downward Omicron cases are providing signs of labor relief.
- BLS Long-haul Truckload Employment indicates February surge in employment –
not all are drivers but signs show an early boost to labor in transportation.
Policy

- The infrastructure bill could have a significant impact on supply chains
and labor sources.
- Future spikes in COVID-19 infections may cause additional unknown
regulations.
- The future of driver supply and the downstream impact of continued part
disruptions are unknown.
- There is an administration push for private businesses, continuing to ease supply
chain congestion – getting workers back into workforce will be key.
- Border crossing congestions continue to be an issue with Texas border delays.


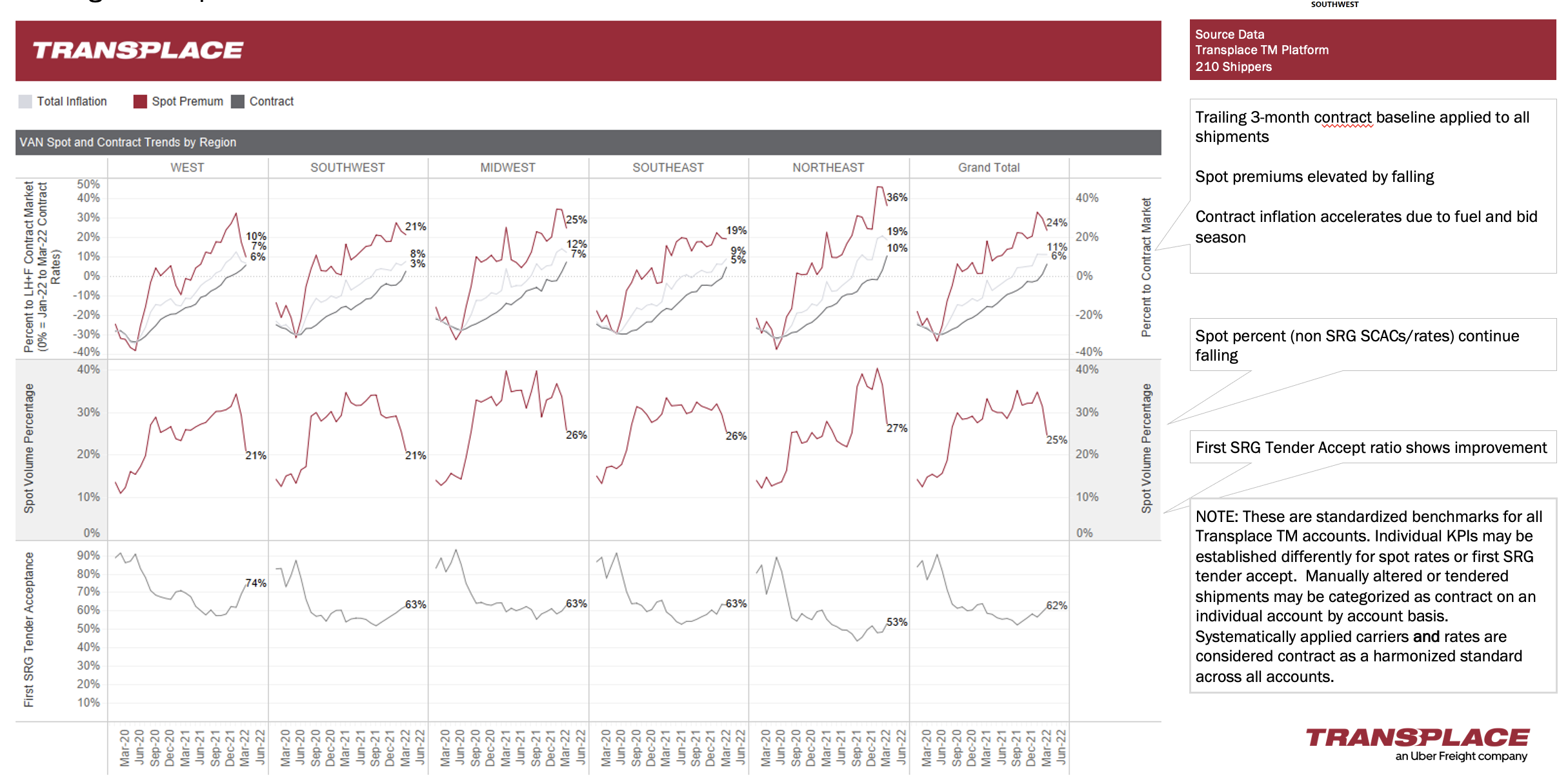
Spot premiums remain in elevated status across all modes
Transplace analyzes our ~$15 billion of Freight Under Management (FUM), the largest shipper-carrier network in the world, to identify trends in spot and contract rates.
Take action now and plan for what's ahead
Scroll to the right to see recommended actions across all major modes and geographies.
U.S. - Full Truckload
- Significant spot rate and volume drop
- Contract rate inflation due to recent bids and fuel
- Capacity in flux
- High volatility expected 2022
- Seasonality, lease defaults and Shanghai reopening are big unknowns on state of
capacity in 2022 Q2



U.S. - Less than Truckload (LTL)

- Record operating ratios for many public LTL carriers
- Continued rate inflation expectations for 2022
- Signs of demand leveling, but most carriers are near capacity
- Carriers continue to create more capacity through terminal growth
and expansion
U.S. - Intermodal

- Drayage showing signs of loosening and still having driver shortage issues
- Equipment street dwell remains a focus for all providers
- International bullwhip creating volatility concerns if softer conditions
- Flat rate expectations into late 2022, early 2023
U.S. - Bulk

- Raw material shortages causing shutdowns and emergency plans
- High single to double-digit rate increase requests as capacity shortages limit
options
- Average lead times down to 12 days vs 14 days
- Tight capacity with slight improvement of tender accepts
Mexico - Truckload

- B1 visas increasing migration of drivers to U.S. companies
- Export orientated economy continues
- Inflationary impacts on driver wages due to labor and retention
- Texas border backlog leading to estimate $100MM USD loss per day ends with - U.S.-MX agreement: 1-week backlog expected
Canada - Truckload/LTL

- Unexpected strong economic conditions driving rates upward
- Vaccine mandate offered greater disruption that anticipated increasing broker
volumes and prices
- Historic fuel prices
- CPI inflation at four-decade high
International – Ocean & Air
- LA/LB container queue down from ~100 in Jan 22 to ~40 now
- Shanghai lockdown extensions still in place past April 4 expectations
- U.S. suspends normal trade relations with Russia and Belarus
- More East Coast congestion than west driven by ILWU and West Coast
congestion
Europe

- Tight markets prevail mainly due to driver shortages
- EU mobility package exacerbates driver shortage with various restrictions
- Erratic movement of fuel cost leading to additional ‘crisis’ FSC
- Russia-Ukraine conflict impacting growth. German recession risk.
- Record employment is strong, but declining PMI figures